The Food and Agriculture Organisation of the United Nations for a world without hunger (FAO) class Edible Insects as a “protein with a lighter environmental footprint”.
I was aware of this eating insect/bug narrative through the promotion of Nicole Kidman “eating bugs” in 2021, an attempt to make eating bugs look attractive and to normalise this behaviour. That narrative has bubbled to the “in your face” surface now as highlighted in Episode 355 of The Highwire covering recent German Farmer Protests and connecting that to insects farming. This war against our food supply has been going on long before 2024.
Crafting the Narrative
Follow along the timeline from the bottom and notice the target market shifting, the groups who first get excited, the investors and more. It starts with “inspired” college roommates, investors are “attracted”, the “movement” has capital now to “market” and build, then the United Nations gets on board [allegedly].
It appears to have started in 2006 with the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organisation releasing a report titled Livestock’s Long Shadow which is being quoted that by 2050 Glgbal demand for meat will double, where “livestock production accounts already for 70% of all agricultural land”. Based on these trusted numbers alternative, sustainable protein sources have been pushed from January 2012 conference.
The “growing drive to bring insects into Western shopping baskets” took off in 2013 following FAO’s Edible Insects report . They are “rich in protein; environmentally friendly to harvest; sustainable; and, they’re already eaten, and enjoyed, in many other parts of the world.”
Setting the stage for the next superfood, packed with nutrition!: “‘Crickets are up to 70 per cent protein, which is three times the amount of protein found in beef. They’ve also got more iron than spinach, more calcium than milk, and the list keeps going. They are an incredible superfood.”
The Gateway Insect: “Crickets are the most widely cultivated insects for the human diet across the world and are considered the ‘gateway bug’ for people who choose to eat insects.”
Link to pages driving the “eat bugs” agenda:
- The Journal of Insects as Food and Feed (JIFF) launched May 2014 – READ
- First “Insects to feed the world” conference May 2014 – REF
- United Nations Food & Agriculture Organisation (FAO) – leads the global charge on edible insects – WEB
- International Platform of Insects for Food and Feed (IPIFF) circa 2014 – Promoting Insects for Human Consumption – HERE
Climate Change
The climate change agenda is driving the “eat bugs” agenda. What the media won’t tell you – HERE

This page is attempting to trace back where this climate-driven food agenda began, and how it has evolved. The timeline will be continuously updated as articles and links come to my attention.
Links in reverse chronological order
2024
March 25, 2024 – Chief Nerd: Lab-Grown’ Meat Made Inside Bioreactors Is Now Being Tested at Restaurants in the U.S. – WATCH
January 2024 – The Highwire Episode 355: UNREDACTED – WATCH, The Jaxen Report: Edible Insects in the context of Davos 2024 – EXCERPT
2024 – Sustainable Protein Sources (2nd Edition) – Advances for Healthier Tomorrow: Chapter 25 – Edible Insects: a Neglected and Promising Food Source – READ
- “The interest in insects as human food in the Western world is increasingly considered a viable alternative to other protein sources. In tropical countries, it is common practice and about 2000 insect species are eaten. Insects emit low levels of greenhouse gases, need little water, and require limited agricultural land.”
2023
December 1, 2023 – Brian Sussman Show – Ep 20 – Latest Climate Plan: “No Meat For You!” and more – WATCH
December 2023? – WHO Tedros – wants us to “transform food system” to combat “climate change” – TWEET
October 4, 2023 – Liberty & FinanceL Farms Being Shutdown; We Must Resist | Alex Newman – WATCH, READ
- The UN Master Plan for Humanity
September 25, 2023 – Epoch TV: No Farmers No Food: Will You Eat The Bugs? | Documentary – WATCH
July 13, 2023 – FreedomFest 2023 | Alex Newman: The Global War on Farmers and Push to “Eat The Bugs” – READ, TWEET, CREDIT
- Epoch Times: ‘No Farmers No Food’ Documentary Panel Discussion Held at FreedomFest – READ
July 9, 2023 – 41st Annual Meeting of Doctors for Disaster Preparedness: Let Them Eat Bugs – Debbie Bacigalupi – WATCH
2022
October 19, 2022 – Daily Mail: Aldi considers selling edible INSECTS to help families through the cost-of-living crisis – READ, Summit News – CREDIT
- Butget supermarket Aldi in the UK is considering stocking ‘edible’ bugs and providing recipe kits for parents to prepare worms and crickets for their hungry children, to solve “poverty”. Bugs are “known” to be “a cheap and sustainable form of protein”.
- The supermarket is also involved with a TV game show in which insect ‘farmers’ will pitch the bugs as the ‘next big thing’
- Yum Bug founders Aaron Thomas and Leo Taylor, both 28, are competing against other start-ups to get their product on the supermarket’s shelves
September 2, 2022 – The Guardian: UK urges hunger-stricken African nations to farm insects – READ
July 20, 2022 – Rebel News: Elites want us to eat bugs: Montrealers take a taste test – READ
- A new ideology that governments want to indoctrinate citizens with is one claiming that if we want to save the planet, we will have to turn to alternative sources of protein. Alternative sources such as insects, of course.
July 16, 2022 – WEF: You Will Eat Bugs, and You Will Be Happy – WATCH
June 27, 2022 – London Free Press: By Jiminy! Feds put $8.5M into London cricket farm – Aspire cricket manufacturing farm – READ
- $8.5 million of taxpayer money will go toward construction costs and technology — artificial intelligence specifically — that will monitor the billions of crickets about to be turned into food. The facility starts in a few days.
- byproducts will be sold back to area farmers as fertilizer
- Mohammed Ashour, co-founder and chief executive of Aspire Foods, an idea that began nine years ago (2013) as a project with four other McGill University students who, in essence, want to solve the problem of world hunger.
- 5 MBA students from McGill University “entered the world’s largest and most prestigious social enterprise competition” the 2013 Challenge The Global Food Crisis, which they won the Clinton Global Initiative Hult Prize in 2013 – About –REF
May 30, 2022 – Daily Mail: Would you eat bug bolognese? Primary school children in Wales could be offered EDIBLE INSECTS including mealworms and crickets as scientists urge the next generation to embrace eco-friendly meat substitutes – READ
May 26, 2022 – Canadian Manufacturing: Aspire Food Group completes production of manufacturing facility in London, Ontario – to produce 9000 metric tons of crickets every year for human and pet consumption – READ, CREDIT
- Aspire: A world transformed by insect technology – WEB, “Crickets are nature’s superfood ingredient for healthier, happier pets” – READ
- Eventually, 13 million kilograms of crickets will be processed annually in London. – REF
February 9, 2022 – WEF | Climate Change | Davos 2022 Agenda: 5 reasons why eating insects could reduce climate change – “Before you say “yuck,” hear us out.” – READ, You will Eat Bugs – WATCH
- Edible insects can produce equivalent amounts of quality protein when compared to animals – not all but, crickets, certain ant species and mealworms are known to be protein and calorie dense stars in the the insect-consumption world.
- Insects require less care and upkeep than livestock – they use less resources, less than plants!! [Plants use CO2 and produce oxygen – it appears they want to take our plants too!]
- We’re actually running out of protein – The demand for protein will exceed our ability to procure it with10 bn people by 2050 [Well if the taking land, well yes!]
- Insects are part of a virtuous eco-cycle – circular agriculture – feed microlivestock landfill waste!
- . You can start small and work your way up – consume animals raised on insects!
January 14, 2022 – Frontiers in Sustainable Food Systems: Review: Insects—A Source of Safe and Sustainable Food?— “Jein” (Yes and No) – Grabowski et al – READ, some definitions
- “The role of the consumer is the final factor that justifies the idea of producing insect-based foodstuffs or not…the effort in producing it is futile when the consumer simply does not eat it”
2021
December 30, 2021 – Summit News: Vanderbilt University Professor Argues That We All Need To Eat BUGS – “Black soldier fly larvae, in particular, hold promise.”, follow the EU example – READ
October 22, 2021 – PHYS: Eating the right insects can provide nutrition, and might be good for the planet – READ
- According to UN FAO “Some 2 billion people around the world already eat insects to supplement their diet”
- A January 2021 study in Critical Reviews in Food Science Nutrition said edible insects may have “high superior health benefits”
July 12, 2021 – WEF: Why we need to give insects the role they deserve in our food systems – READ
May 9, 2021 – The Guardian: If we want to save the planet, the future of food is insects – READ
- Ref the EAT-Lancet Commission report (see Jan 2019)
April 9, 2021 – FAO: Food safety aspects of edible insects outlined in new publication – READ, ARCHIVE,
- Looking at edible insects from a food safety perspective – Challenges and opportunities for the sector – REPORT
- “FINANCIAL INVESTMENTS: Despite growing interest in the sector, procuring investments can be difficult for start-up companies owing to unclear regulations about the production and commercializationof insects as food and feed. This may also have implications on the advancement of research and development in the field.”
- “overcoming food neophobia among some consumers, especially in the Western countries, is a challenge for the edible insects sector”

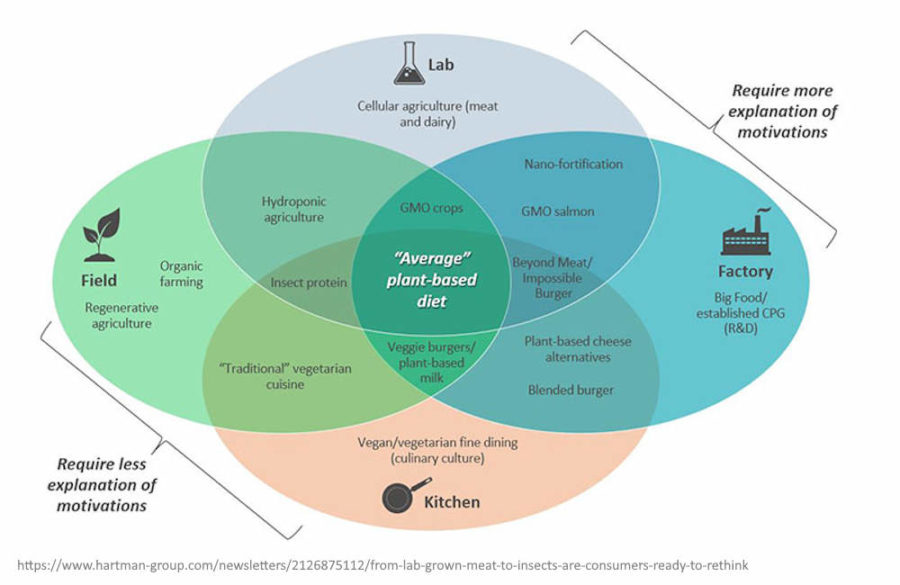
May 11, 2021 – Wired: The Cicadas Are Coming. Let’s Eat Them! – Why not embrace Brood X as the free-range, sustainable source of protein that it truly is? – READ, The Hartman Group – CREDIT
- Edible insects have been a part of rich culinary traditions around the world for years, from Mexico’s crunchy chapulines to beondegi, Korea’s silkworm pupae street food
- Market researchers predict the global edible insect market will reach $4.63 billion by 2027, with North America as the fastest-growing sector – ARCHIVE, now Edible Insects Market Worth $9.60 Billion by 2030 – READ
January 14, 2021 – Summit News: EU’s food safety agency Gives Go-ahead For Eating WORMS – “Allergic reactions are likely to occur”. – ARCHIVE, Mealworm consideration – ARCHIVES
January 2021 – Edible Insects Market by Product (Whole Insect, Insect Powder, Insect Meal, Insect Oil) Insect Type (Crickets, Black Soldier Fly, Mealworms), Application (Animal Feed, Protein Bar and Shakes, Bakery, Confectionery, Beverages) – Global Forecast to 2027 by Meticulous Market Research Pvt. Ltd- READ, CREDIT
- Market researchers predict the global edible insect market will reach $4.63 billion by 2027, with North America as the fastest-growing sector – ARCHIVE, Updated Jun 2022 – Edible Insects Market Worth $9.60 Billion by 2030 – READ
- Based on insect type, the crickets segment is expected to dominate the edible insects market during the forecast period of 2020-2027 (In terms of value) – REF
2020
December 22, 2020 – IOP Science | Environ. Res. Lett. : A review of edible insect industrialization: scales of production and implications for sustainability – Wade et al – READ
- “Edible insects have emerged in the past decade as a sustainable alternative to agro-industrial production systems and livestock-based diets.” [see below what has driven this!]
December 17, 2020 – FAO releases a comprehensive guide to sustainable cricket farming – READ, PDF
September 9, 2020 – Runtastic: Eating Insects Might Be Your New Favorite Source of Protein – READ, the WEF refered to this blog post as a “study”- HERE, the blog links to Sep 2015 paper – HERE
- With over 2,100 types of edible insects to choose from
- The WEF want you to know that insects offer between 9.96-35.2 g of protein/100g c.f 16.8-20.6 g/100g for meat. They forgot to state “per edible protein”, and that insects vary.
May 13, 2020 – Euractiv: Insect-based feedstuffs hold ‘enormous potential’ for EU sustainability goals – Farm to Fork strategy “will support the creation of “sustainable and novel feed materials and food,” listing insects as one such potential innovation….“To reduce the environmental and climate impact of animal production,…” – READ
- 2022 Food Safety: Farm to Fork strategy – for a fair, healthy and environmentally-friendly food system – at the heart of the Green New Deal- ARCHIVE
April 3, 2020 – Guardian: Edible insects set to be approved by EU in ‘breakthrough moment’ – READ
- EU’s European Food Safety Authority is expected by the insect industry to endorse whole or ground mealworms, lesser mealworms, locusts, crickets and grasshoppers as being safe for human consumption.
February 18, 2020 – Hartman Group: The Big Bet on Bugs. Providing Palatable Alternative Proteins for Consumers – READ
- Food manufacturers are betting that new protein sources are likely to become increasingly attractive alternatives as more consumers are making a conscious decision to eat less meat [Thus any threat to dis-belief of the climate narrative threatens bug investments]
January 5, 2021 – Critical Reviews in Food Science Nutrition: Potential health benefits of edible insects – Nowakowski et al – READ, CREDIT
- “Edible insects may have superior health benefits due to their high levels of vitamin B12, iron, zinc, fiber, essential amino acids, omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, and antioxidants.”
2019
October 15, 2019 – The Hartman Group | Research: From Lab-Grown Meat to Insects: Are Consumers Ready to Rethink Protein? – READ
- A wide range of protein possibilities are emerging, including those in the increasingly popular plant-based category but also those that are genetically modified, derived from cell-cultured meats, or derived from insects
- Food & Technology 2019: From Plant-Based to Lab-Grown – REPORT “As more consumers than ever question the health, ethical, and environmental implications of animal products…”
September 12, 2019 – WEF: A psychologist explains why we find some food disgusting – and why it matters – Insects and lab grown meat ” is a promising area for social marketing.” – READ
August 21, 2019 – World Economic Forum: This London insect farm is changing the way we eat | Pioneers for Our Planet – WATCH
- A company called Entocycle feeds brewery waste and old coffee grains to fly larvae to create a form of animal feed that doesn’t harm the environment. “Insects are nature’s perfect upcycling machines,” says founder Keiran Whitaker. “They create organic natural protein that we can feed to animals – and eventually humans.”
July 8, 2019 – PLOS one : A parasitological evaluation of edible insects and their role in the transmission of parasitic diseases to humans and animals – READ, CREDIT
June 28, 2019 – The Coversation: Eating insects is good for you — and the planet! – READ
- UN FAO: How to Feed the World in 2050 – PDF
June 2019 – ARUP Report “The Future of Urban Consumption in a 1.5°C World’ – READ, PDF, C40 – READ, The Highwire Ep 357 – EXCERPT, European Farmers are protesting in 2024, moving global – TIMELINE
- Expose News: By 2030 you will not eat meat and you will be allowed only three items of new clothing a year, report says – CREDIT,
- Ambitious target is ZERO meat and milk consumption per day, yet you will still get 2,500kcal/day!
May 5, 2019 – Wired: Save the Lemurs! Eat the Crickets! -To take pressure off endangered lemurs, researchers are encouraging the people of Madagascar to embrace bugs as a source of protein. – READ Lab grown food revolution
January 16, 2019 – The Lancet | Commissions from the Lancet journals: Food in the Anthropocene: the EAT–Lancet Commission on healthy diets from sustainable food systems – READ, The Guardian – CREDIT
- The EAT–Lancet Commission is the first full scientific review of what constitutes a healthy diet from a sustainable food system,… Sponsored by the Wellcome Trust!
- The EAT-Lancet Commission Summary Report – “Transformation to healthy diets by 2050 will require substantial dietary shifts…”- READ, PDF
2018
January 29, 2018 – Time: No One Elegantly Devours a Four-Course Meal of Bugs Like Nicole Kidman – READ, In a Vanity Fair video, Kidman reveals that her “hidden talent is eating microlivestock,” i.e. Nicole Kidman Eats Bugs – WATCH
2017
April 1, 2017 – Wageninger University: List of edible insects of the world – READ, PDF
2016
November 10, 2016 – WEF: What will we eat in 2030? “or new alternatives (soya products, or perhaps insects or artificial meat)” – ARCHIVE
April 8, 2016 – The Guardian: The worm has turned: how British insect farms could spawn a food revolution – “With meat prices expected to soar, agricultural entrepreneurs believe invertebrate livestock can provide the protein we need. But will the mainstream ever be ready to eat mealworms?” – READ
July 2016 – North American Coalition for Insect Agriculture (NACIA) is formed in 2016 when 50 stakeholders in the insects for food and feed industry met at the Eating Insects Detroit Conference – READ, REF
- Initially North American Edible Insect Coalition (NAEIC) – heads the “BugAg” movement. The mission of the North American Coalition for Insect Agriculture is to encourage positive use of farmed insects in North America.
May 26-28, 2016 – Eating Insects Conference at Wayne State University in Detroit – the first conference dedicated solely to exploring the culture of edible insects to be held in the U.S – READ, REF
April 27, 2016 – PROteINSECT Final Conference: Insects as a Sustainable Source of Protein – Feed for the Future – Brussels. An EU funded FP7 project. (Grant #312084) , coordinated by Fera Science Ltd in the United Kingdom – AGENDA, READ, White Paper – PDF
- PROteINSECT – enabling the exploitation of insects as a sustainable source of protein for animal feed and human nutrition – READ,
- WHITE PAPER: Insect Protein: Feed for the Future – Addressing the need for feeds of the future today – PDF
- Fera Science Press Release: Insects no more risky than other proteins as animal feed – ARCHIVE
- Maggots raised on animal manure could provide a sustainable alternative to animal feed – READ
March 7, 2016 – Wired: You’ll Eat Bugs. These Investors Are Betting Millions on It – 3 years ago (2013) two college room mates (Greg Sewitz and Gabi Lewis) ordered 2 boxes of live crickets for their pet but instead made protein bars! – READ, ARCHIVE
- Investors: “…one deep-pocketed group is taking the pair quite seriously. Today Sewitz and Lewis’ company, Exo Protien, announced it has raised $4 million in a series A round of funding led by Accel Foods with participation by investors like Collaborative Fund.
- “…the United Nations says insects could play a crucial role in feeding a growing global population without wrecking the environment”
2015
September 16, 2015 – European Journal of Clinical Nutrition: Are edible insects more or less ‘healthy’ than commonly consumed meats? A comparison using two nutrient profiling models developed to combat over- and undernutrition by Raye et al – READ, Indirectly referenced by WEF (point 1) – HERE
- “The results presented here are the first systematic comparison of the nutritional composition of insects and meat, and their relative healthiness according to contemporary nutrient profiling models.”
- “Insect nutritional composition is highly diverse in comparison with commonly consumed meats. The food category ‘insects’ contains some foods that could potentially exacerbate diet-related public health problems related to over-nutrition, but may be effective in combating under-nutrition.”
July 7, 2015 – Financial Times – Edible insect farms strive for scale – READ, REF,
- Next Millennium Farms (now Entomo Farms) is one of a number of bug farms that have sprung into being to supply food brands and chefs with insects to bake into protein bars, biscuits and other bug delicacies.
- A revision to the EU’s Novel Foods Regulation, due this year, puts edible bug farmers in the right place at the right time.
June 2015 – EU: Updating rules on novel foods to keep up with scientific advances – new category for insects proposed – PDF
March 26, 2015 – Documentary: America’s Shrinking Farms – TRAILER, ARCHIVE, “That Will Change Your Views on the Future of Food” – READ, UN FAO – CREDIT
March 20, 2015 – EcoWatch “Transforming Green” via UN FAO: Are insects the next climate-friendly superfood? – READ, ARCHIVE, SOURCE
- “Demand for food-grade insects is growing rapidly,” says the website for Tiny Farms, a Silicon Valley-based start-up “pioneering the industry production of insects.”…Currently, it admits, edible insects are a niche products with the cost of a pound of cricket flour ranging from $25-$45. But it says that’s due to lack of scale and it hopes to change that”
- “More than 30 companies are already using cricket flour in their products such as cookies and energy bars. [and you didn’t know it!] And while eating insects is common in Latin America, southeast Asia and parts of Africa because they’re a cheaply available commodity,” in the US its not.
- The same day “Obama Signs Executive Order to Cut Government Greenhouse Gas Emissions by 40 Percent by 2025 – READ, REF
March 18, 2015 – Food Navigator: Tiny Farms: Edible insects are a novelty today, but they’ll be mainstream tomorrow – ARCHIVE cricket flour producers are popping up everywhere.
February 24, 2015 – Lux Research: Alternative Proteins to Claim a Third of the Market by 2054 – “insects, algae, and synthetic biology sources may make up over 50% of the alternative protein market by 2054” – ARCHIVE
- “Shifts in supply and demand of protein for human consumption will drive the rise of alternative proteins to 307 million MT by 2054, initiating significant changes in the food and agriculture landscape.” [what will drive that “demand”?]
February 15, 2015 – TEDxYoungstown: Alternative Protein | Kevin Bachhuber founder of Big Cricket Farms, the first urban edible insect farm in the US – WATCH, ARCHIVE
2014
December 10, 2014 – Consumer Reoprts: Cricket-flour protein bars pass the taste test – Consumer Reports’ experts munched on snack bars and cookies – READ, CREDIT
- Protein products aimed at people interested in a paleo diet or weight loss in general are becoming increasingly popular, and cricket flour is seen as an environmentally efficient way of getting that nutrient in your diet”
- “These critters are raised on domestic cricket farms, where they are fed a grain-based diet. They’re dried or roasted and then milled into a fine flour. About 40 crickets are packed into an average snack bar.”
- “Cricket-flour goodies attracted plenty of attention at the recent Natural Products Expo in Baltimore, where manufacturers claimed they are making an investment in the environment because the insects don’t require much land or water—certainly much less than cattle, for example.”
August 20, 2014 – Washington Post: Gateway bug: How crickets could hook America on eating insects – ARCHIVE
June 24, 2014 – Practical Ethics: Should Vegetarians Consider Eating Insects? – READ
- “In the last few years, there has been a push from various bodies—including the UN—to get Western countries to adopt eating insects as an alternative to meat. They are: rich in protein; environmentally friendly to harvest; sustainable; and, they’re already eaten, and enjoyed, in many other parts of the world.”
May 14-17, 2014 – FAO: 1st International Conference “Insects to feed the world” at Wageningen University in the Netherlands – A whole new sector in animal livestock – READ, WATCH, Conference report – PDF, READ
- Summary Reoprt – “The overall objective of the conference was to lay the foundations for continued dialogue, further research, evidence-based policy making and investments to promote the use of insects as human food and as animal feed in the context of food and feed security”. – PDF

- The first international conference on insects for food and feed brought over 450 participants from 45 countries together to discuss about the state of the art in research, business and policy making in this new developing sector.
- “Today more than 20,000 cricket farmers are registered in Thailand alone” Patrick Durst, FAO
- A new Journal of Insects as Food and Feed (JIFF) by Wageningen Academic Publishers was also launched – READ, First edition – HERE
- Foreword: Why a Journal of Insects as Food and Feed? – READ
March 17, 2014 – Wired: Out in the Open: Raise Your Own Edible Insects With This Free Kit – cockroaches, crickets, mealworms and silkworms – a “new and growing community of people who treat insects as food” known as entomophagy – READ
- Daniel Imrie-Situnayake and Tiny Farms have created what they call Open Bug Farm — a high-tech kit for raising your own edible insects.
- In 2016 Mark Zuckerberg’s sister Arielle at a veture capital firm invested in Tiny Farms – READ
January 23, 2014 – US Patent 2014/0020630: METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR BREEDING FLYING INSECTS (Filed Jul 18, 2012) – PDF, CREDIT
2013
September 2013 – EcoWatch “Transforming Green” news began – A “cutting-edge news service”… “EcoWatch became a Certified B Corporation and joined more than 900 companies that leverage the power of business to solve social and environmental problems.” – ARCHIVE
May 14, 2013 – NPR | The Salt: Maybe It’s Time To Swap Burgers For Bugs, Says U.N. – READ
- The Food and Agriculture Organization has been pondering bugs as a protein source since 2003, but in the new report, the agency argues that insects might be essential to feeding a planet of 7 billion people.
- FAO says the future is bright for edible insects. “Although it will require considerable convincing to reverse [feelings of disgust], it is not an impossible feat,”
May 13, 2013 – BBC: UN Report urges people to eat insects to fight world hunger – READ
May 13, 2013 – Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations | FAO Forestry Paper 171: Edible insects: Future prospects for food and feed security – Report – ARCHIVE, (also see Jan 2012) The Highwire Ep 355 – CREDIT, Refered to as a “Landmark” report – REF
- Agenda to get Western nations to switch over to consuming insects – propaganda campaign to make this happen COMMUNICATIONS: “Western societies require tailored media communication strategies and educational programmes that address the disgust factor. Influencing the public at large as well as policymakers and investors in the food and feed sectors by providing validated information on the potential of insects as food and feed sources can help to push insects higher on political, investment and research agendas worldwide.” pg xv
- “The Way Forward” – “Recent developments in research and development show edible insects to be a promising alternative for the conventional production of meat, either for direct human consumption or for indirect use as feedstock. Nevertheless, a tremendous amount of work still needs to be done by a wide range of stakeholders over many years to fully realize the potential that insects offer for food and feed security.” – PDF
- The roadmap drawn up during the Expert Consultation Meeting on Assessing the Potential of Insects as Food and Feed in Assuring Food Security in Rome in January 23-25, 2012 – the tasks tha lay ahead
May 13, 2013 – FAO PRESS RELEASE: Forest products critical to fight hunger – including insects – New study highlights role of insects for food and feed consumption. – READ
- FAO’s research, done in partnership with Wageningen University in the Netherlands
- The Barriers:
- “legislation in most industrialized nations forbids the actual feeding of waste materials and slurry or swill to animals, even though this would be the material that insects normally feed on. Further research would be necessary, especially as regards the raising of insects on waste streams. But it is widely understood by scientists that insects are so biologically different from mammals that it is highly unlikely that insect diseases could be transmitted to humans.”
- Regulations often also bar using insects in food for human consumption
- “The private sector is ready to invest in insect farming. We have huge opportunities before us,” said Paul Vantomme, one of the authors of the report. “But until there is clarity in the legal sphere, no major business is going to take the risk to invest funds when the laws remains unclear or actually hinders development of this new sector,”
May 13-15, 2013 – International Conference on Forests for Food Security and Nutrition in Rome – READ, Opening Remerks – PDF
- FAO launched their new study on Edible Insects – (see above)
- “It is estimated that insects form part of the traditional diets of at least 2 billion people. Insect gathering and farming can offer employment and cash income, for now mostly at the household level but also potentially in industrial operations.”

May 8, 2013 – Jason Drew and AgriProtein Team Wins United Nations Award for Innovation for Africa – nutrient recycling – a method that uses waste and fly larvae to produce natural animal feed – READ [The prelude to human insect farming?]
May 2013 – UN FAO – Edible Forest Insects – ARCHIVE
May 2013 – UN FAP -REPORT: Six-legged livestock: Edible insect farming, collection and marketing in Thailand – ARCHIVE
- Eating and selling edible insects are common activities in Thialand either farmed or harvested in the wild. Cricket farming was introduced >15 years ago (c. 1996). “However, information remains scant on their current stauts and on production, technology development, market channels and business ventures as well as future opportuinties.
- Crickets and Palm weevil larvae are farmed. “Currently there are approximately 20,000 farms operating 217,529 rearing pens. Total production over the last six years (1996-2011) has averaged around 7,500 tonnes per year”
April 24, 2013 – Wellcome Collection: Insects Au Gratin- Explore the future of food, debate the consumption of insects as a potential alternative to traditional livestock, and watch a live 3D food-printing demo. – READ
- There’s a “growing drive to bring insects into Western shopping baskets” [This is before the FAO report launch!]
2013 – Clinton Global Initiative | The Hutt Prize Solving “The global food crisis” challenge – ARCHIVE, Won by McGill Univertity students for Aspire cricket farming.
2013 – International Platform of Insects for Food and Feed (IPIFF) is a non-profit organisation founded in 2013 which represents the interests interests of private players in the insect industry associated to this organisation. In order “to help the insect industry prosper in Europe and worldwide” – ARCHIVE, READ, IPIFF today – HERE
2012
2012 – Tiny Farms, an edible insect company, was founded in 2012 to address a growing and evolving global market in entomophagy; the human consumption of insects. Promoting Entoculture is the intersection of bugs, food and farming – ARCHIVE
- “Insect production is more energy, space and time efficient than traditional agriculture, making it ideal for a world where more than half the population live in cities.”
- entomophagy movemement is a revolution in food production
August 28, 2012 – NPR | The Salt:Grow Your Own Locust Kit Could Someday Help Feed African Refugees – two industrial engineering students want to use insects as emergency food – READ, Design award – ARCHIVE, WATCH
- The product is still in the preliminary stages of development, but from what we can tell, it’s the first of its kind [the begnining/inspiration for benchtop, household tiny farms?]
May 9, 2012 – Incredible Edible Bugs – there is a movement is afoot to encourage insect eating – video 1 – ARCHIVE
January 2012 – Research Gate: Assessing the Potential of Insects as Food and Feed in assuring Food Security SUMMARY REPORT – Conference: FAO Expert Consultation on Assessing the potential of Insects for Food SecurityAt: FAO, Rome, Italy – READ
January 23-25, 2012 – United Nations: Expert Consultation Meeting on Assessing the Potential of Insects as Food and Feed in Assuring Food Security in Rome – READ, REF, Report source – ARCHIVE [Its as though they planned where we are in 2024!]
- Towards a global conference on Edible Insects as Food and Feed (2014) – REF
“Assessing the Potential of Insects as Food and Feed in assuring Food Security” Action Plan: – REF, READ
- Further document the nutritional values of insects in order to promote insects more efficiently as a healthy food source.
- Investigate the sustainability and quantify the environmental impacts of harvesting and farming insects compared with traditional farming and livestock-raising practices.
- Clarify and augment the socio-economic benefits that insect gathering and farming can offer, with a focus on improving the food security of the poorest of society. [then move to all Western society]
- Develop a clear and comprehensive legal framework at the (inter-)national level that can pave the way for more investment, leading towards the full development (from the household scale to the industrial scale) of production and trade in insect products for food and feed internationally.

2011
April 4, 2011 – FAO: FAO’s role in the development of edible insect programmes in collaboration with the Wageningen University- READ, READ, Videos – ARCHIVE
2007
December 2007- Edible Unique – shop online for unique edibles such as insects and other bush tucker – ARCHIVE, c.f. Dec 2015 – ARCHIVE
2006
2006 – United Nations Food and Agriculture Organisation together with The Livestock, Environment & Development (LEAD) Initiative: LIVESTOCK’S LONG SHADOW: environmental issues and options – REPORT, CREDIT
- “The contribution by livestock and especially cattle to environmental problems is on a massive scale and should be addressed with urgency according to FAO’s report Livestock’s Long Shadow. Global demand for livestock products will more than double during the next 50 years (from 229 million tonnes in 1999/2001 to 465 million tonnes by 2050), and livestock production accounts already for 70% of all agricultural land. The livestock sector is an important contributor to greenhouse gas emissions such as CO2, CH4 and N2O.”
- Globally the livestock sector is “one of the largest sources of greenhouse gases and one of the leading causal factors in the loss of biodiversity” …The livestock sector is also a primary player in the agricultural economy, a major provider of livelihoods for the poor and a major determinant of human diet and health. Hence its environmental role needs to be seen in the context of its many different functions…” pg 267
- – FAO 2014 believe Edible insects are a Protein with a lighter environmental footprint – REF

2003
2003 – NPR: “The Food and Agriculture Organization has been pondering bugs as a protein source since 2003” – REF
1997
1997 – Ecology of Food and Nutrition, 36: 347–366: The importance of edible insects in the nutrition and economy of people of the rural areas of Mexico – Ramos Elorduy, J.
- “In Mexico, the protein content of 78 evaluated species ranged from 15 percent to 81 percent of dry matter and protein digestibility ranged from 76 percent to 98 percent” – pg 70 REF
1996
1996 – Approximate time insect farming was introduced to Thailand, though eating insecst is a historic tradition, the farming isn’t – REF
1992
June 3,1992 – UNCED Earth Summit (Agenda 21) – “sustainable development” becomes the driving force for future global policy and funding. – TIMELINE
1988
1988 – The First International Congress of Ethnobiology was held in Belém, Brazil in 1988 – READ, History – READ, forging interdisciplinary boundaries of anthropology, botany, zoology, archaeology, pharmacology, geography, sociology, linguistics and related fields.
- Presentation: Edible insects: barbarism or solution to the hunger problem? by Ramos Elorduy, J
(In D.A. Posey & W.L. Overal, eds. Ethnobiology: implications and applications. Proceedings of the First International Congress of Ethnobiology, pp. 151–158. Bélem, Brazil, Museu Paraense Emílio Goeldi.) – REF
1983
December 19, 1983 – UN establishes a “governing council” that would become known as the “Brndland Commission” – “Process of preparation of the Environmental Perspective to the Year 2000 and Beyond” – TIMELINE
- UNEP recommended the UN establishment of a “Special Commission” to “make available a report on environment and the global problamatique to the year 2000 and beyond, including proposed strategies for sustainable development”. Gro Harlem Brundtland was appointed as Chair
- In 1987 the commission published their report titled Our Common Future, where they cemented the term “sustainable development”. This document formed the basis for the 1992 first UN Earth Summit (UNCED).
1976
May 31 – June 11, 1976 – UN Habitat I conference – Vancouver Declaration on Human Settlements – READ, TIMELINE
- The Declaration provided the first definition of ‘adequate shelter’ and recommendations for each country to achieve it. Population, land use and resources officially become a “concern”.





