So much of our history on immunisation, vaccines and vaccination is not taught, loosely taught, forgotten or lost in the archives.
This page is simply at place to log historical papers and quotes relating to the history of ‘vaccines’ and the pursuit of finding the perfect tools for inducing artificial immunity. The timeline helps reveal how “the science” unfolded. As I discover a relevant piece of information I log it below in a timeline format.
I’m especially interested to find out when in our history the terms vaccine and vaccination, became so generally used. The terms were coined by Edward Jenner and were specific to the scarification-inoculation of cowpox to achieve “immunity” to smallpox, prior to this scarification-inoculation was called variolation – the only thing that changed was the “virus” toxin used. It appears Pasteur and the discovery of bacteriology capitalised on the well established procedure of “vaccination” and began using the terminology for their pursuit in generating artificial immunity to all manner of disease-causing bacteria.
It’s fascinating to see how far we have come, but also how tightly we have held onto the beliefs of hundreds of years ago.
Some historic quotes
1893: The second greatest step taken in medical science – creating “vaccines”:
“The discovery that microbes may change their characters and are capable of transformation by artificial means into vaccines of fixed and ascertained power is without doubt the greatest step which has been taken in medical science since disease-producing microbes were first studied.
The task which then presented itself to investigators was that of discovering the germs of contagion which were recognised as being the cause of disease and of elaborating substances protective against them
Opening paragraph of Haffkine’s lecture on Injections Against Cholera (1893)
Thus in 1893, the minds of “medical science” have latched onto the process:
- Step 1: Discover the germ of contagion that cause the disease
- Step 2: Artificially transform that germ into ‘vaccines’
1897: The purpose of ‘vaccination’:
The object of all vaccination processes is, first, to achieve a degree of immunity which shall be equal or greater to that which accrues to a patient who undergoes and recovers from an actual attack of the disease; and, secondly, to achieve that immunity without any risk to life or health.
Principles upon which the proposed method of typhoid vaccination is based (1897) – REF
Louis Pasteur was a French chemist who is created the development of the first vaccines for both rabies and anthrax in late 1800s, he is credited with founding the “science of immunisation”.
Historical immune hunting data points in reverse chronological order
You may want to scroll to the bottom and work you way up through time…content is constantly being added.
2024
May 10, 2024 – A Midwestern Doctor Substack: The Forgotten Science of Vaccine Disease Provocation – Why do vaccines cause people to get the diseases they are supposed to protect you against? (History within) – READ
- How vaccination can (and has through history) cause increased risk of infection
2022
October 26, 2022 – A Midwestern Doctor Substack: Why Do Vaccines Consistently Fail to Prevent Disease Transmission? – Original Antigenic Sin – READ and Pandemic strategies designed to test compliance not prevent death
2016
February 2, 2016 – Nature: Immunological memory: lessons from the past and a look to the future – Baber, Zinkernagel et al – READ [Understanding of immunology is still evolving]
- “… immunologists are yet to fully appreciate the mechanisms that control memory responses in the immune system. [The very principle underlying “immunization” is not understood – so how can long-term “effective” be claimed]
- Furthermore, our definition of immunological memory itself continues to evolve, with recent suggestions that innate immune cells also show memory-like behaviour.”
2015
October 12-16, 2015 – WHO Expert Committee on Biological Standardization: Collaborative study: Calibration of Replacement International Standard for Diphtheria Toxoid for use in Flocculation Test – PDF using the Ramon flocculation method – WHO MORE
- “Diphtheria is caused by exotoxin-producing strains of the bacterium Corynebacterium diphtheriae. Active immunization against diphtheria is based on the use of diphtheria toxoid (DTxd), a chemically detoxified preparation of diphtheria toxin, to induce protective antibody responses.”
- DTxd is produced by growing the toxin-producing C. diphtheriae in liquid media and converting the toxin to inactive toxoid by treatment with formaldehyde. Antigenic strength and purity of the bulk toxoid is evaluated by measurement of ‘limit of flocculation’ (Lf) units….”… “Due to its simplicity, speed and economy, flocculation remains the primary method used by vaccine manufacturers to evaluate toxin and toxoid concentrations in Lf.”
- In the original Ramon flocculation method the antigen concentration is kept constant and different amounts of antitoxin are added to a series of tubes…
- WHO: The 1st International Reference Reagent of Diphtheria Toxoid for Flocculation Test (DIFT) was established in 1989 and update 2007 “following depletion of stocks”
February 20, 2015 – The Wall Street Journal: The Return of the Vaccine Wars- The controversy over vaccines is as old as vaccination itself (amid “the current measles outbreak”)- READ, ARCHIVE,
- Dec 2014: “The anti-vaccination epidemic: “Whooping cough, mumps and measles are making an alarming comeback, thanks to seriously misguided parents “- by Paul Offit – ARCHIVE
- “Almost 8,000 cases of pertussis, better known as whooping cough, have been reported to California’s Public Health Department so far this year.” [Dr Offit appears “misguided”, he of all people should know that Pertussis bacteria are not prevented from colonising in a pertussis-vaccinated person, the Warfel et al 2014 Baboon studies showed that, thus the vaccine will not prevent “cases”, and will not prevent vaccinated kids from spreading the disease to their unvaccinated infant siblings.]
2002
August 1, 2002 – Current Opinion in Immunology: On differences between immunity and immunological memory – Rolf M Zinkernagel – READ
- “Over the past 10–15 years, many reviews and experiments have been published to document that immunological memory is antigen-independent.”…but only few have recently argued that protection by immunological memory is antigen-dependent”
- [ “The Science” is being debated, so not settled. The pool of “evidence” assessed is always limited by the types of experiments that are “allowed” to be conducted/funded.]
- “…points of view are based on discrepant definitions and perceptions of what the immune system is or should be about”
- “Immunity—that is, protection against infection or re-infection” [So Immunity is not protection against “disease” (the symptoms) but against “infection”, does this mean the prevention of colonisation of a target pathogen?]
2001
Search for new Vaccines with more antigens (less jabs, more diseases), less side effects
October 12, 2001 – Vaccine: The role of the adsorption process for production and control combined adsorbed vaccines – Matheis et al – READ
- “One intention for the development of new vaccines is to get an increasing acceptance for vaccinations. This shall be achieved:
- first by production of vaccines with less side effects (e.g. acellular pertussis vaccines
- secondly by new combinations with a higher number of antigens resulting in a reduced number of injections.
1998
December 21, 1998 – FDA approved a new recombinant Lyme vaccine, LYMErix™, which reduced new infections in vaccinated adults by nearly 80%...3 years later, the manufacturer voluntarily withdrew its product from the market amidst media coverage, fears of vaccine side-effects, and declining sales” – (2007) The Lyme vaccine: A cautionary tale – READ, MWD – CREDIT
- Vaccine was promoted “safe & effective”, but because of media coverage, not mandated (less sales) and the legal ability to sue the manufacture, the “safe and effective” product was withdrawn!
1997
August 6, 1997- JAMA | Vol 278, No. 5 : Biological Warfare: A Historical Perspective – Christopher et al (Military). pp 412-417- PDF Anthrax vaccine etc
- “Smallpox was used as a biological weapon against Native Americans in the 18th century. During the French and Indian War (1754-1767), Sir Jeffrey Amherst, commander of British forces in North America, suggested the deliberate use of smallpox to“reduce”Native American tribes hostile to the British”
- “In the United States, an offensive biological program was begun in 1942 under the direction of a civilian agency, the War Reserve Service. The program included a research and development facility at Camp Detrick, Md. (renamed Fort Detrick in 1956), testing sites in Mississippi and Utah, and a production facility in Terre Haute, Ind. Experiments were conducted using pathogens, including B anthracis [anthrax] and Brucella suis.“…”5,000 bombs filled with B anthracis spores were produced at a pilot plant at Camp Detrick” but not used.
- “…a program to develop countermeasures, including vaccines, anti-sera, and therapeutic agents to protect troops from possible biological attack,was begun in 1953.”… Human experimentation using military and civilian volunteers was initiated in 1955.” – Challenge studies!
- Following Nixon’s termination of the “US offensive program from 1969-1970, biological defense in the US military has focused on the development of countermeasures including detection capabilities, personal protective equipment, vaccines, diagnostics, and therapies to protect our military members”
- A Fifth Review Conference of the Biological and Toxin Weapons Convention was due to be held in 2001. Re UN inspections of research facilities not granted in Russia and Iraq.
- Note 1997 article mentioned upcoming 2001 conference. This took place Nov 19, 2001, following the “anthrax letter” incidence, but disagreement caused it to be postponed until Nov 6, 2002, where the Convention looked at “the Prohibition of the Development, Production and Stockpiling of Bacteriological (Biological) Weapons and on Their Destruction” …”pathogenic microorganisms and toxins”, [not viruses?] – PDF, READ, 2-6th UN Review Conferences (1986-2006) – ARCHIVE
- United Nations Office for Disarmament Affairs (UNODA) was established January 1998 – REF
1996
April 5, 1996 – Science: Immunological Memory and Protective Immunity: Understanding Their Relation – Ahmed & Gray – READ, CREDIT
- …there is still considerable debate regarding the mechanisms by which long-term immunity is maintained.”
1984
1984 – Antibodies, their structure and function by Steward – READ [Understanding the state of Immunology pre global vaccine ramp-up]
- In the decade or so following von Behring and Kiasoto’s 1890 antitoxin early observations “it was demonstrated that antibodies could specifically lyse bacteria (bacteriolysis), precipitate bacteria and agglutinate bacteria (cause them to clump together).” It was also shown antibodies could be produced against non-toxic substances such as proteins
- It would appear any product that elicits an antibody responce can be called a “vaccine”. Thus a vaccine’s “effectiveness” is too often measured by antibody titres, likely Immunoglobulin G (IgG) as this is “quantitatively the most important serum immunoglobulin and its major function is to neutralize toxins, viruses and to bind to and optimize bacteria[l]…phagocytosis and elimination”.
- “IgG is the only immunoglobulin to cross the human placenta and is thus a major defence mechanism against infection in the early part of the infant’s life”.

1982
September 1982 – Senator Paula Hawkins (of Florida) proposed a Bill amid public’s heightened concern for adverse events associated with the pertussis (Whooping Cough) vaccine, administered as DTP, the bill was withdrawn – REF
- In follow up to Senator Hawkins’ request for more information on April 26, 1983 the US Dept HHS held an open meeting on”Pertussis and Pertussis Vaccines” regarding the pertussis dilemma – REF
- In September1981 an oral pertussis vaccine was developed and trialled in Germany with less side effiects [I didn’t know that!] – REF
1977
April 4, 1977 Science magazine (quote) by Dr Jonas Salk – REF
The live poliovirus vaccine has bee the predominant cause of domestically arising cases of paralytic poliomyelitis in the United States since 1972. To avoid the occurrance of such cases, it would be necessary to discontinue the routine use of live polio vaccine
Dr Jonas Salk
1973
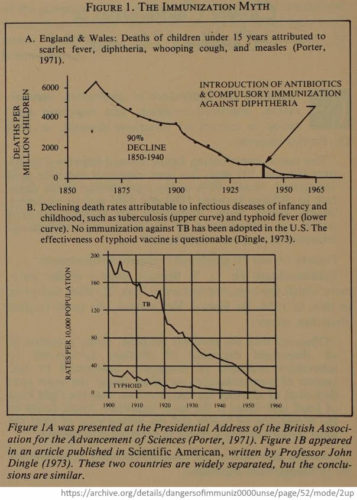
1973 – The Immunization Myth – Two diseases that declined without mandated vaccine (TB & Typhoid) – REF
1959
1959 – BOOK: Clonal Selection Theory of Acquired Immunity by Sir Frank Macfarlane Burnet – READ
- “If we take any ‘good’ antigen, either soluble or particulate, for which we have a convenient in vitro method of titrating the corresponding antibody and inoculate a series of animals, it will usually be a simple matter to show the characteristic difference between primary and secondary response” – REF
1955
July 1955 – Tri-State Medical Journal: Poliomyelitis Vaccine – Brodie versus Salk – by Dr Fred Klenner – READ
- “Klenner tells how the versatile vitamin C dealt most efficiently with the polio problem during earlier epidemics”- REF
1955 – US Military: Between 1951-1955 the anthrax vaccine was developed, using “alum” as the “placebo” – PDF, SOURCE, A year later (1956) Camp Detrick, the US military biological weapons research facility was renamed Fort Detrick – TIMELINE
- 5 years later the first anthrax outbreak in the Twentieth Century happened to occur! Stanly Plotkins et al – READ, READ
1953
1953 – British Pharmacopoeia 1953 edition – READ (see 1932)
- This is the publication with the Australian Therapeutics Goods regulator uses.
- Smallpox vaccine no longer referred to as “vaccine lymph” because it can be made in chicken embryos! – REF, no longer “cow pox” – REF
- Biological products now include “Bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) vaccine, Scarlet Fever Antitoxin, Scarlet Fever Prophylactic, Dick Control, and Dick Test Toxin”- REF [are they rolling all things under the banner “vaccine”?]
- Vaccines available in 1953 – READ, “bacterial vaccine” – READ

Viral vaccines include smallpox and yellow fever.

1949
March 1949 – Can. J. Comparative Medicine Vet Sci.: Twenty-five years ago, a veterinarian, Gaston Ramon discovered toxoids [in 1923] (French Canadian), Panisset – READ, PDF, CREDIT
1941
September 13, 1941 – The Lancet: Preparation of Alum-precipitated toxoid for use as an immunising agent – Barr, Glenny, Pope, Linggood – READ
1939
1939 – The year the first antibotic, Penicillin, is mass produced and released to the world, changing the practice of medicine forever. Following Gerhard Domagk’s 1935 work which inspired the Rockefeller funded search for simple compound drugs. – TIMELINE
1938
September 20, 1938 – An Electrophoretic Study of Immune Sera and Purified Antibody Preparation by Arne Tiselius and Elvin A Kabat (Sweden) – PDF
- It was not until 1938 that “significant advances” in the knowledge of chemical nature of antibodies were made. “At this time, Tiselius and Kobat demonstrated that the antibody activity of an antiserum is associated with the gamma-glogulin (γ) fraction of the serum. – via electrophoresis work developed by Tiselius during 1937 – REF
- Globulins which function as antibodies are today known as “immunoglobulins“.
1938 – 58 British physicians signed a memorial against compulsory immunizations in Guernsey, and “were able to point to the virtual disappearance of diphtheria in Sweden without any immunization” yet Germany with compulsory immunizations diphtheria cases increased – REF
1937
Tiselius develops the Electrophoresis technique for separating, and characterising proteins – Demonstrating that antitoxin serum is made up of many “serum globulins” i.e. Antibodies
September 1937 – Biochemistry Journal: Electrophoresis of serum globulin: Electrophoretic analysis of normal and immune sera – Tiselius – READ, PDF, CREDIT
- “By subjecting serum to prolonged electrophoresis, and collecting the slowest fractions, a serum globulin material was isolated which was different from those obtained by the common methods and more homogeneous than these.”
- “The first experiments with the new apparatus showed very clearly that different fractions of serum globulin…consisted of several components, migrating at distinctly different rates.” Tiselius named them these serumglobulins by the lower-case Greek aphabet symbols for Alpha, Beta, Gamma and Delta.
February 1937 – Biochemical Jorunal: Electrophoresis of serum globulin. I – Arne Tiselius – READ, CREDIT
- Concluding that serum is not a “homogeneous substance as judged by electrochemical properties”
January 25, 1937 – Transactions of the Faraday Society: A New Apparatus for Electrophoretic Analysis of Colloidal Mixtures by Arne Tiselius – READ, CREDIT
- Tiselius’ work on Electrophoresis dates back to his 1926-30 Thesis – READ
1935
Basic structure of viruses is discovered
1935 – In 1935 Stanley isolated a crystalline protein possessing the properties of tobacco mosaic virus. It contained two substances, ribonucleic acid (RNA) and protein. The simple structure characteristic of tobacco mosaic virus was soon found to be a basic property of many human viruses such as coxsackie virus (which I believe to be the cause of Multiple Sclerosis), Echo and polioviruses — they all contain only ribonucleic acid and protein – (F. Klenner 1971) – REF
- There exist minor variations. Adenoviruses contain desoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and protein. Other viruses such as that causing influenza contain added lipid and polysaccharides. DNA is used to program the large viruses, like mumps, RNA is used to program the small viruses, like measles.
- The role of the protein coat is to protect the parasitic but unstable nucleic acid as it rides the “blood highway” or “lymphatic system” to gain specific cell entry.
- Pure viral nucleic acid without its protein coat can be inactivated by constituents of normal blood.”
January 1, 1935 Journal of Immunology: Active Immunization in Monkeys Against Poliomyelitis with Germicidally Inactivated Virus – Maurice Brodie – READ, LEAD
- “These experiments demonstrate that a proper dose of formalized virus may produce, in the majority of monkeys, an active immunity sufficient to enable them to withstand intracerebral inoculation of one or more infective doses of virus, and that virus treated with formalin is a better antigen than is phenolized virus.”
- His projects were eventually “cancelled as a result of complications from vaccine trials resulting in the death of 6 participants and the paralysis of 10 others. The resulting public outrage delayed further research on the polio vaccine until the 1950s, when the Salk and Sabin vaccines were produced” – WIKI
1935 – In 1935 Gerhard Domagk demonstrated that simple chemical compounds could be used to treat and cure invading bacterial infections, such as his use of Prontosil, to cured systemic Streptococal infections. This work sparked a search for anti-bacterial drugs.- REF, REF [needs more info] Prontosil testing began in 1932.
- Domagk’s worked at the German IG Farben/Bayer and was responsible for testing new compounds for antimicrobial activity. (As virtually all disease were considered due to bacteria) The dye- coal-tar drug industry are the historical foundation of chemical drugs used as medicines throughout the 1800s into 1900s and today.
- Prontosil is a sulfa drug, or sulfonamides, all of which are related to the compound sulfanilamide. It provided the first successful (antibiotic) drug therapies for many bacterial diseases. Domagk’s “sulfonamide drug…paved the way for the antibiotic revolution in medicine,”
- Domagk’s discovery of the antibacterial properties of Prontosil won him the 1939 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, the year Penicillin was mass produced. He would not officially receive the award until 1947, after WWII – REF, REF
1932
1932 – British Pharmacopoeia 1932 edition – READ
- There as only smallpox and anti-typhoid-paratyphoid vaccines – REF
- Diphtheria and Tetanus were antitoxin serums – REF
- Alum – REF, Potassium alum (potash alum) – READ, The precursor for aluminium adjuvant
1931
1931 – Journal of Pathology and Bacteriology: Rate of disappearance of diphtheria toxoid injected into rabbits and guinea pigs: Toxoid precipitated with alum – Glenny et al – READ (aluminium potassium sulphate – REF)
- “Glenny Pope Waddington and Wallace 1926 first demonstrated the high antigenic efficiency of diphtheria toxioid to which potach alum had been added and stated …that such a suspension constituted one of the best antigens so far used by them. These authors further showed that a suspension of an alum toxoid precipitated after boining for an hour was as efficient an antigenic properties as the average toxin-antitoxin mixtures for human immunisation against diphtheria.”
1929
May 10, 1929 – British Journal of Experimental Pathology: On the Antibacterial Action of Cultures of a Penicillium, with Special Reference to their Use in the Isolation of B. influenzæ by Alexander Fleming – READ, From the Laboratories of the Inoculation Department, St Mary’s Hospital, London. History of Fleming CREDIT
- “It is clear, therefore, that the production of this antibacterial substance is not common to all moulds or to all types of penicillium.”
- Bacillus influenzae is Pfeiffer’s bacillus (a bacterium) which was thought to be the cause the 1918 Influenza pandemic. They even made a “vaccine” for Pfeiffer’s bacillus. Today the bacterium is classified as Haemophilus influenzae.
- Fleming accidentally discovers the anti-bacterial power of the fungus Penicillum notatum, but it wouldn’t be until 1939 that Howard Florey et al at Oxford University with Rockefeller Foundation funding that goes to work isolating the fungus chemical secretions and formulated the first, mass produced “antibiotic” know as Penicillin, in time for World War II, thanks to collaborations with British pharmaceutical companies. By the end of the war it was nicknamed “the wonder drug”. – REF
- Florey’s work is inspred by Gerhard Domagk (1935) work who showed injecting simple chemical compound, Prontosil, cured systemic Streptococal infections – demonstrating invading bacteria (infections) can be treated – and the search for chemical drugs with Fleming’s work. – REF
- Alexander Fleming was knighted in 1944 and shared the Nobel prize for Physiology or Medicine in 1945 with Florey and Ernst Boris Chain – READ
- Its curious how Robert Malone, the discoverer of RNAs ability to elicit an immune respose, thus it’s potential as a “vaccine”, was not granted a share in the 2023 Nobel Prize for the pseudouridine, the reason modified mRNA can evade the immune system and thus be considered a new type of “vaccine”!
1926
Mixing potassium Alum with toxoid first demonstrated to increase antigenic power of vaccine – (adjuvant is discovered)
September 21, 1926 – New Britain herald – Your Health – How to Keep It – Causes of Illness . The first of a serise of 5 articles on diphtheria by Morris Fishbein – Editor or JAMA and Hygeia the Health Magazine –READ
- New Discoveries…sanitarians and hygienists are convinced that diphtheria may be completely eliminated from our country through the application of our present knowledge…
- The application will depend on the enlightened attitude of the public which will avail itself of the knowledge that has been disseminated among physicians”
- “When ignorance, superstition, and prejudice prevail” says American Association of Medical Progress (lobby group?) “preventable diseases will be allowed to slay right and left , and especially among children”
January 12, 1926 – The UK Guardian: New vaccines for tetanus and diphtheria – French discovery | Immunity claimed for infants – READ
- “Vaccines” against diphtheria and tetanus, comparable as prophylactics with Jenner’s vaccine against smallpox, have been discovered at the Pasteur Institute here by a French chemist, M. G. Ramon.
- Two years ago experiments began with anatoxins upon human beings at the Pasteur hospital and the military hospital in Paris.
1926 -Journal of Pathology and Bacteriology: The influence of optimal proportions of antigen and antibody in the serum precipitation reaction Dean and Webb – READ
1926 – Journal of Pathology and Bacteriology Vol 29, Iss 1: Immunological notes. XVII–XXIV (17-24) by Glenny, Pope, Waddington and Wallace from the Wellcome labs – READ, PDF cont. from Vol 28 p 482 – READ (Glenny and Pope still working on this in 1941) [And so begins the aluminium adjuvanted toxoid vaccines]
- “Glenny Pope Waddington and Wallace 1926 first demonstrated the high antigenic efficiency of diphtheria toxioid to which potach alum had been added and stated …that such a suspension constituted one of the best antigens so far used by them. These authors further showed that a suspension of an alum toxoid precipitated after boining for an hour was as efficient an antigenic properties as the average toxin-antitoxin mixtures for human immunisation against diphtheria.” – (1931) – REF (note potash alum is potasium alum)

- 17 – The Antigenic Value of the Toxin-Antitoxin Precipitate of Ramon
- 18 – Destruction of toxin by heating in the presence of phenol
- 19 – Destruction of toxin by heating in the presence of Trikresol
- 20 – The effect of evaporation of toxin-antitoxin mixtures
- 21 – The effect of formaldehyde on diphtheria antitoxic serum
- 22 – The antigenic value of precipitated toxoid
- 23 – The antigenic value of toxoid precipitated with potassium alum –
An emulsion of such a precipitate has high antigenic properties - 24 – The antigenic value of toxoid that will not flocculate in the presence of antitoxin
1926 – Combined Schick test and diphtheria prophylactic; combined diphtheria-scarlet-fever prophylactic – Glenny and Waddington – READ (COMBINING antigens!)
- “A preparation that would give a satisfactory Schick reaction and at the same time act as an immunising agent would have a distinct advantage …reduce the number of subsequent prophylactic injections for human beings from 3 to 2.”
1925
Glenny et al prolific work on Diphtheria toxin looking for antigenic power for a “vaccine”. Diphtheria and Tetanus combined. Terminology: TOXIN, TOXOID AND ANTITOXIN
July 1925 – Journal of Pathology and Bacteriology Volume 28, Issue 3: Immunological notes. VIII.-XVI (8-16)- Glenny, Pope, Waddington and Wallace – READ, PDF
- 8 – Comparison between in vitro and in vivo methods of testing diphtheria antitoxin
- 9 – Two zones of flocculation in Ramon tests
- 10 – The relation between antigenic value and dose injected of toxin-antitoxin mixtures and of modified toxin
- 11 – The stability of diphtheria toxin used for the Schick Test
- 12 – The destruction of dilutions of diphtheria toxin of Schick strength by shaking
- 13 – The action of phenol on mixtures of toxin and antitoxin
- 14 – The stability of toxin-antitoxin mixtures
- 15 – Some discrepant in vivo titration of antitoxin – batch variation
- 16 – A method of producing tetanus antitoxic serum of high potency
April 1925 – Journal of Pathology and Bacteriology Volume 28, Issue 2: Immunological notes. I.-VII, (1-7) Glenny, Pope, Waddington and Wallace – READ – Development of our work on immunity
- “In the present series of notes we see indications of how a minute but repeated stimulus of toxin may produce immunity; there is an obvious link between this fact and naturally acquired immunity in man…” immunity of diphtheria is studies.
April 1925 – Journal of Pathology and Bacteriology Volume 28, Issue 2: The titration of diphtheria toxin by the flocculation method – Glenny & Wallace – READ

- “The use of Trevan microsyringe enables small volumes of antitoxin to be measured accurately…”
April 1925 – Journal of Pathology and Bacteriology Volume 28, Issue 2: The measurment of the combining power of diphtheria toxin and toxoid with antitoxin in relation to their antigenic efficacy – A. T. Glenny, C. G. Pope, Hilda Waddington – READ, PDF – TERMINOLOGY: TOXIN, TOXOID AND ANTITOXIN
- The word “toxin” as used by immunologists possesses more than one interpretation….used in a specific sense the term signifies a definite substance which is one of the active principle …responsible for pathological symptoms.”
- “For the present we are using the expression “toxoid” for that modification of specific toxin which causes no pathological symptoms in animals, but is capable of combining with antitoxin and for stimulating the production of immunity” i.e. toxin-antitoxin mixture
- Recently, Ramon (1924) has suggested the term “anatoxine” without defining whether this term should be applied generally or specifically and without making clear whether the word replaces “modified toxin” or “specific toxoid” or both.
- “Different brews of diphtheria toxin vary both in their degree of toxicity and in their power to stimulate the production of antitoxin. It is of importance therefore to be able to measure both the toxicity of the brew and its immunising value…The recent establishment of the flocculation test (Ramon 1922, 1923 and 1924) gives us another new and important method of measuring the strength of a toxin.” [The flocculation test is still used today]

[Alum is discovered in 1926 to begin the aluminium adjuvant toxoid “vaccines”!]
April 1925 – Journal of Pathology and Bacteriology Volume 28, Issue 2: The antigenic effect of intravenous injection of diphtheria toxin – Glenny and Pope –READ (pre-adjuvant days) – toxin-antitoxin mixture injected gave as good response as subcutaneous
- …it appears to have been generally accepted that animals cannot be successfully immunised by intravenous injection of diphtheria toxin” [alone]
- “Most of the work in the past on the time of fixation of diphtheria toxin has been done by subcutaneous injection..” – (same author diff paper same J edition – REF)
- This paper shows “…however the circumstances in which immunity response follows intravenous injection”…mix antitoxin with the toxoid called “modified toxin partially neutralised with antitoxin“
1924
The year anatoxin was coined (formaldehyde treated toxin) and “indicated” for “vaccination of children”
April 1924 – Experimental Biology and Medicine: Immunity results obtained in school children with diphtheria toxoid (modified toxin) and with 1/10 L+ mixtures of toxin-antitoxin – A. Zingher, M. Park et al – READ, CREDIT
January 1924 – Annales de l’Institut Pasteur, 1924, Vol 38 Iss 1 p.1: “Sur La Toxine Et Sur L’Anatoxine Diphtheriques” – G. Ramon – READ, REF, REF2, Title: On Toxin and on Diphtheria Anatoxin – Flocculating Power and Immunizing Properties by G. Ramon (Translated from French),
- Ramon introduces a new term “anatoxine” i.e. anatoxin (de-toxified toxin), the Ramon flocculation test which is still in used today though modified, and he suggests anatoxin is indicated for “vaccination of children”
- Diphtheria toxin in the flocculation reaction: “With particular regard to the toxin, its flocculating power can therefore be measured by the quantity of antitoxin [antibody] necessary for its saturation, or in other words by the quantity of antitoxin which causes the appearance of the initial flocculation.”…”the toxin always requires, in order to flocculate, the quantity of antitoxin which saturated it on the ninth day of culture;”…What we observe here regarding the toxins leads us even further to believe that there is perhaps another quality in the serums that Ehrlich’s method does not indicate.
- “Special case of diphtheria toxin made non-toxic (Diphtheria anatoxin)“- by adding formaldehyde
- “As we have indicated, we always add, to the toxin which we use in our various in vitro dosages, a small amount of formaldehyde… with the aim of avoiding cultures that would be made possible by inevitable contamination during handling…”..It is this [formaldehyde treated toxin] product that we propose to call diphtheria anatoxin. (i.e.”inverse” of toxic)
- “..we know that anti-diphtheria immunization of guinea pigs is almost impossible with simply diluted diphtheria toxin, difficult with the old method of toxin-liquor mixtures…and very slow and quite inconsistent with the toxin-antitoxin mixture.”
- “Thus the anatoxin derived from diphtheria toxin, of which it may have retained the flocculating and immunizing properties, but of which it no longer has the harmfulness, can generate, in a living organism, immunity and production of antitoxin whose results which precedes allow us to appreciate all the value. This diphtheria toxoid, whose immunizing power will be evaluated in vitro by the flocculation reaction, naturally finds its use in the immunization and hyperi-mmunization of animals.
- …Thanks to its harmlessness and the very high degree of immunity it confers, it also seems indicated for antidiphtheria vaccination in children (1)”
- “(1) The injection, into the subcutaneous cellular tissue, of 0 cc. 25 of diphtheria toxoid, carried out on myself, caused a temporary local redness without any reaction either local or general. This redness was no more pronounced than that caused by the same quantity of boiled toxoid.”
1923
December 1923 – Annales de l’Institut Pasteur Vol 37 Iss 12: Comparative study of the virulence and toxicity of microbial bodies and tuberculin of various samples of tuberculosis bacillus – Exaltation of the virulence of attenuated strains vaccination trials – Borrel et al (French)- READ
- Study has been ongoing for 3 years – isolating various TB strains, These strains were first classified according to their virulence by subcutaneous, intraperitoneal and intra-cardiac inoculation….[early Gain of Function studies!?]
- The first vaccination trials undertaken in 1920 were attempted with a preparation of crushed virulent bacilli….The bacillary mass, freed of alcohol, was suspended in glycerinated water & 50 p. 100 and decanted for a long time. The part placed at the bottom of the vase was used in our vaccination trials…” in guinea pigs
December 1923 – Ramon – Annales de l’Institut Pasteur: Flocculation in mixtures of toxin and anti-diphtheria serum, Vol 37, p. 1001 – READ, READ
- “The precipitation reaction described by Ramon (1923) for the titration of diphtheria antitoxin affords an example of the application of the principle in optimal proportions. If either is in excess the formation of precipitate is delayed or inhibited”- REF
1923 – re subcutaneous injection vs intravenous injection of diphtheria toxoid no antibody (antitoxin) formation – REF (pre-adjuvant days)
- Madsen (1923) wrote “according to the published experiments – which are however not very numerous and need revisiting – there is an essential difference in the antitoxic reaction occurring in a horse actively immunised against diphtheria by subcutaneous injection and that occurring as a result of intravenous injection. In the latter mode of procedure the antitoxin formation is almost, nil“
February 2023 – Annales de l’Institut Pasteur: NEW PRINCIPLES OF IMMUNIZATION APPLIED TO VACCINATION THERAPEUTICS by Sir Almroth E. Wright – READ
- “Vaccination can be used during the incubation period of a disease, provided that this incubation period is greater than ten days. This closes the great initial chapter of scientific immunization which was developed by Pasteur.”
1922
November 4, 1922 – JAMA Vol 79 Iss 19: Toxin-antitoxin Immunization against Diphtheria by William H. Parks, pg1584 – READ, CREDIT
1918
1918 “Spanish Flu” pandemic – TIMELINE
1916
November 15, 1916 – Homeopathic Recorder Vol 31: Poliomyelitis-Infantile Paralysis by W Van R. Blighton pg 493 – READ
- On Simon Flexner at Rockefeller instituted working on poliomyelitis…with observations about contagiousness, and public health authorities a frightening people “out of their wits” – AMA is working hard to get the health regulations under their control
- …”we know that fear is a prolific source of disease.”
- “Coming to the subject of the cause of this disease [poliomyelitis], I think my professional brothers will be somewhat startled when I suggest the thought that the present epidemic of infantile paralysis may have been caused by small-pox vaccination. You smile, but why ‘should the disease become epidedemic throughout nearly the entire country so soon after the wholesale process of vaccination?” …since the introduction of compulsory vaccination – tuberculosis has increased 300, skin diseases by 276% , cancer by 600%
The fact is that the rulers of the American Medical Association are laboring so hard to get the health regulations of the country under their exclusive control that they are extending their tyrannical, bureaucratic regulations broadcast over the whole country.
They are assuming to dictate what prophylactic methods and treatment must invariably be used for the promotion of health and the prevention of disease, and yet their teachings in such matters are subject to very frequent changes.
W. Van R. Blighton MD, 1916
1914
1914 – Whole-cell pertussis vaccine released??
- “Jules Bordet and Octave Gengou isolated Bordetella pertussis, a causative agent for whooping cough, in Paris more than 100 years ago, which created an excellent opportunity to invent a vaccine”…In 1914 the whole-cell pertussis vaccine was invented, then in the 1940s it was combined with tetanus and diphtheria toxoids to become DTP” – REF
1913
Berhing toxin-antitoxin inoculation mixture
1913 – Book: Modern Medicine: its theory and practice by Sir William Osler (The Father of Medicine) – Volume 1 – READ , Ch 20 “Diphtheria” Immunization – READ
- In 1913 “vaccination” pertains to ONLY “inoculation of vaccinia”. If any other pathogen is used in an injection it appears to be called “immunization by means of a vaccine” such as in the case of diphtheria – HERE
- “In the Infants’ Hospital in Boston, where children not over two years of age are treated, immunization was commenced in February, 1900.” Using serum
- Immunization by means of vaccine was tried by Petroschky in hundreds of children of whom only one developed diphtheria. Active immunization is still in the experimental stage. Its successful practical use is what is most required for the control of diphtheria.” Page 732 using toxin-antitoxin?
- “Of 12 carriers in our wards, 4 became negative in two weeks by the use of diphtheria vaccine, in doses of 1,000,000 to 10,000,000 every four to six days. Petruschky reported the treatment of 6 cases with injections of diphtheria bacilli killed by chloroform gas.” Page 732
May 8, 1913 – (Translated) German Medical Weekly Vol 39 No. 19, p. 873: About a new anti-diphtheria agent By E. Behring in Marburg (German) – READ, Ramon – CREDIT
- On active immunization against diphtheria. “It is known that Behring’s healing serum was also injected into healthy people to prevent infection, but that this method has had very little success because the undoubted protection only lasts for a very short time and because of the risk of anaphylaxis.”
- On April 18, 1913 “Behring …reported on a new protective agent, consisting of a pure mixture of diphtheria toxin and antitoxin.” Using toxin-antitoxin mixture to treat people prophylactically
- Matthes demonstrated the first human to human serum transfer (passive immunization), providing “much longer lasting protection” than the usually the serum derived from a horse. Mortality from diphtheria is still reported high even with the horse derived serum.
1913 – Schick, B. (1913) Munch. med. Wschr., 60, 2608 – REF, ARCHIVE, The Schick test, developed in 1913, is a skin test used to determine whether or not a person is susceptible to diphtheria – WIKI
- “Schick (1923) when working out the method of diagnosis of susceptibility to diphtheria to which his name is attached injected intra-cutaneously a number of children with a diagnostic dose of diphtheria toxin followed later by a subcutaneous injection of antitoxin.” [should this be 1913? not 1923] re Schick test – REF
1911
Immunology – a new science – educating the public
1911 – The Homeopathic Recorder: “Immunology” – a new science – pg 189 – READ re JAMA – READ
- “Immunology.” — This new word, standing for a new science, is the latest. In brief, it is the science of injecting a product derived from the body of an artificially diseased beast into the body of the human animal to protect the latter from a possible disease.”
- “If a healthy wayfaring man were to start on a journey and come near another man with diphtheria, he would, if in care of the latest in modern medicine, receive a hypodermic injection of antitoxin, or several of them, according to the enthusiasm of his mentor. Passing on to the next town he might run into typhoid, in the next into the plague, and so on into cholera, tetanus, hydrophobia, small-pox, and possibly into some other diseases, for each of which he would receive into what was once a healthy body a different product from diseased animals for each disease” – The practical application of immunology
February 25, 2011 JAMA : Immunology: A medical science developed through animal experimentation by Dr. F. P. Gay – READ, READ The step by step development of immunology
CLICK for notes on Immunology a new medical science:
- One of 17 pamphlets written for the Council on Defense of Medical Research of the American Medical Association to educate the public – “taking up the relations of animal experimentation to ethics, diagnosis, cancer, vaccination, the live stock industry, tuberculosis, typhoid, dysentery, plague, rabies, surgery, internal secretions, circulation of the blood, tropical diseases, etc.”
- “Perhaps no other of the medical sciences can be so suitably discussed in relation to animal experimentation as immunology, because no other science has been so dependent on this method of attack for its development….The science of immunity, or immunology… indeed, parallels bacteriology both in chronology and in method.
- “The relatively recent development of any exact knowledge of the mechanism of immunity is at first glance surprising, when we consider that certain examples of natural and of acquired resistance to disease have been recognized since ancient times.”
- “The first and most wide-spread type of resistance to disease is the inborn or natural immunity which is evident on the initial exposure to a given malady.”
- “Logical deduction from these observed instances of acquired immunity long since led to attempts to reproduce this advantageous condition artificially.
- “It is well known that the Chinese and other peoples of the East protected themselves from smallpox: by variolization, which was effected by inserting the scabs of human smallpox lesions in the nose of healthy individuals.” [That’s new!]
- “A similar method was introduced into England by Lady Mary Wortley Montague in 1721 and was employed until the observations of Jenner on the relation of cowpox to smallpox in 1798 led to the present method of prevention of the disease by vaccination. The chance that a disease of cattle (vaccinia) is intimately related to a fatal human disease and that an attack of the one in the form of a localized disease would protect against the more generalized malady, alone rendered Jenner’s observation fruitful.
- “No generalized conception of the principle of “vaccination with a virus of diminished virulence,” as later established by Pasteur, however, existed.
- “The discovery of the fundamental principles of bacteriology by Pasteur and Koch, the isolation and cultivation of bacteria in pure culture, and the proved etiologic relation of a definite micro-organism to a given disease, gave new impetus to the principle of vaccination exploited by Jenner. The work of Pasteur and his pupils with the bacillus of chicken cholera on animals laid the foundation for the discovery of the great principle of vaccination by means of bacterial cultures of diminished virulence.
- “Theories of immunity were offered by Pasteur, Koch and others, but they were based largely on speculation drawn from the bare results of infection rather than from experiments designed to expose the process of immunity itself….
- “It remained for Metchnikoff, a biologist, to give the first experimenial evidence explanatory of the process of immunity. In 1882 Metchnikoff began recording his observations on the function of the white blood corpuscles in protecting the body from disease,…
1911 – The Homeopathic Recorder: US Army dispatched to Mexico were “inoculated with vaccine to protect them from typhoid fever” pg 186- READ
- “The Japanese medical corps “sent men to investigate and test the water, food and camp-grounds of their army, while the American medical scientists vaccinate and, presumably, assume that the men can drink infected water, eat bad food, have unsanitary camps, and escape all the consequences of these… Typhoid vaccination at best is but an experiment, an unwise thing to make on an army that may be badly needed, and an unjust thing to the human beings who have no choice in the matter.”
1911 – The Homeopathic Recorder: The Tuberculin “Test” (State Boards of Health) falses sense of secuity for diagnosing tuberculosis p 520 – READ
- The “chief objections are that it is positive in the presence of the slightest infections…on the other hand, be negative and fail to disclose a case of generalized tuberculosis…dependence on this test may lull authorities and the public into a sense of false security”… “A large amount of evidence has now accumulated in regard to the uses and limitations of the tuberculin test both in man and animals” (Lancet Sept 16, 1911)
1910
The year The Flexner Report was released!
September 17, 1910 – The Lancet: Vaccine Therapy: Its Administration, Value, and Limitations by Sir Almroth E. Wright pg 863 – READ, (via) Homeopathic Recorder (1911): The practice of “Vaccine Therapy” was introduced by Sir E.A. Wright about 6 yrs ago [c. 1904]- READ
- “As he [Wright] clearly shows, too much importance is frequently attributed to the presence of a particular microbe, when, as a matter of fact, the condition may be due to a mixed infection, and this, in his opinion, accounts for the failure of vaccine treatment in many instances”
- The Homeopath writes “All of this reads like the preliminary obituary of the Vaccine Therapy”
- [1910 The Lancet Vol 1″Theory of Opsonins” Wright pg 1738 – REF]
- “Opsonins were discovered and named “opsonins” in 1904 by Wright and Douglas, who found that incubating bacteria with blood plasma enabled phagocytes to phagocytose (and thereby destroy) the bacteria”. – WIKI
July 1910 – The Homeopathic Recorder: “Serum Sickness” officially becomes a new term in medicine – READ
- The serum therapy “should be given in close intervals and not at intervals of several days” and “there is no way of knowing beforehand that a person is hypersensitive” [state medical science!]
- “The fact is that the manufacturers have skillfully worked the public up to the point where it is safer to give it regardless of effects rather than have a case die without it. It is a case of scientific advertising“
1910 – The Homeopathic Recorder: Anti-Typhoid Vaccination – READ
- JAMA states US Army favors this vaccination – of 1,000 cases,122 had no reaction, 908 had mild, 60 moderate and 10 severe reactions.
- Homepaths state: “Consider a man vaccinated against small-pox, against typoid, against tuberculosis, rabies, tetanus and serveral other diseases, does anyone in his heart believe that that man can retain his health under the strain? Imagine a regiment vaccinated against everything for which a vaccine has been prepared, and another left to nature and a common sense sanitarian, would any sporting man put his money on the “protected” regiment?”
1910 – The Homeopathic Recorder – Antitetanic serum (Tetanus) – a comment to the JAMA works as a prophylactic but not as a treatment just trust us – READ
April 1910 – “By 1910, when C. V. Chapin published his classic book on The Sources and Modes of Infection, the role of the human carrier [of disease] was well established” – REF
“It now appears that the growth of disease germs outside of the body is not frequent enough to be an important factor in the causation of disease, but their growth in the body without causing sickness, their latency as it were, often for many months, is a factor of very great significance…
While some of the following pages may seem rather radical to many, I believe that practically all laboratory workers will agree with the contents of the first chapter, and that a large number of bacteriologists and health officers are convinced of the great importance of “carriers” and mild unrecognized cases.”
Influenza: “The rapidity with which epidemic influenza spreads, its sudden contemporaneous appearance at many distant points, and the difficulty of tracing the route of infection, render it almost certain that there must in this disease be many mild atypical cases, and many persons infected, but showing no symptoms.” – (1916) – REF
January 25, 1910 – (via) N.Y. State Journal of Medicine: Experimental Poliomyelitis by Simon Flexner – READ
CLICK – Notes for how Simon Flexner determines poliomyelitis is “infectious” and caused by a “virus” micro-organism too small to see under the microscope.
- Presentation of the “experimental study into the causation and pathology of epidemic poliomyelitis”,which has been epidemic for 3 years (“first” appeared 1907 according to Flexner, but history show such disease symptoms appeared in 1840).
- “Until recently it has been a disputed question whether or not poliomyelitis is an infectious disease…It is an infectious disease. It is caused by a minute micro-organism that has not certainly been seen under the microscope, but yet can be defined and studied as though it were visible. It is still an open question whether poliomyelitis is a contagious disease…”
- “Severe cases of it arise among adults as well as among infants and children.”
- In 1907 we had at the Rockefeller Institute our first access to cases of poliomyelitis…[via] spinal fluids, removed by lumbar puncture…” but failed to “convey the disease” to lower animals or monkeys. 1909 the disease reappeared in a “localised epidemic” and gained access to spinal cord of 2 deceased children.
- “The introduction of the intra-cerebral mode of inoculation has removed all difficulties in the way of continuous transfer of the virus from one monkey to another….It has been transferred [via brain injection] from animal to animal without break and has passed through a considerable number of monkeys… Thus it has been proven in a relatively short time that epidemic poliomyelitis is an infectious disease and is due to a living virus [poison], because we know of no disease that can be successively transferred through a long series of animals which is not due to a living virus; and therefore, we have a right to assert that the cause of this disease is definitely a micro-organism quite as much as the bacillus of tuberculosis is the cause of tuberculosis.”
- “Now, the effects in the monkey are like those in the human being. After the injection of the virus [spinal fluid], which is made through a trephine opening in an etherized animal, and after the animal recovers from the etherization, there is a period varying considerably in length — the shortest time being four days and the longest time thirty-three days — during which the animals appear quite normal. As a rule when the monkeys become sick they become sick very quickly”
- We have studied this virus in various ways and have made out the class to which it belongs. It is an example of the so-called filterable virus. The organisms constituting it are so small they cannot be resolved under the microscope and are small enough to pass through Berkefeld earthen filter. [and a Chamberland filter] …Hence it must be classed among the filterable viruses of which we now know several causing diseases in animals and at least one other causing a disease in human beings.”…it belongs to the class of highly resistant viruses or organisms that include the virus of rabies and of vaccinia.”
- Regarding immunity, “We have ascertained that we cannot reinoculate an animal that has recovered from the disease itself” but only challenged after 4 months…long term is unknown. It is predicted due to the “class” of virus that “a very strong immunity will be rendered by a single attack of poliomyelitis”…”The testing of such a prediction would be rather difficult, because luckily, until recent years, we have been spared these epidemics. It appears, however, that they are becoming more frequent, not only in this country, but in Europe, and that epidemics have been more common in the last ten years than in all previous times as far as we can tell.” [The era when “vaccination” from animal products (serum/antitoxin etc) increased?]
- “I am sorry I can say nothing to you concerning a therapy of this condition, because nothing has been accomplished in that particular direction…I can offer nothing at the present time in the way of treatment.” [maybe they should consult the homeopaths!!!]
- “I wish I could tell you something definite concerning the way in which this virus gets into and out of the body, but our knowledge on this point is still very fragmentary and it will have to be increased before we can institute proper measures of prevention of the disease” !
- “I wish now to state that it is not improbable that the mode of entrance and exit of this poison may be the same as the mode of entrance and exit of the poison which causes epidemic cerebro-spinal meningitis, and the two diseases may be disseminated in much the same way.” [note Flexner uses the words “virus” and “poison” interchangably]
- “Epidemic poliomyelitis reaches its height at mid-summer” [when more insects come out and toxic chemicals are used to try to control them?]
Now, it is to be hoped that we have entered upon an era-of knowledge respecting the disease… that whatever knowledge we have now secured and are promised in the future, grows out of the fact that animals have been used for experimental purposes for the benefit of the human race in the investigation of this disease
Dr Simon Flexner, on using animals to test their “science”
1908
July 17, 1908 – Homeopathic Recorder – Doesn’t Believe in Pasteur by Mont. R. Leverson MD – READ
- Did Pasteur steal the “germ theroy” from Professor A. Bechamps “Les grande Problemes Medicaux” ?[READ] where he proposed the “microbic theory of disease, “la plus grande sottise scientifique de ce temps” (the greatest scientific stupidity of this time) – REF
- Major Medical Problems ( Les grande Problemes Medicaux) – concerning the History of so-called organisms (French) the evolution of Bechamp’s own research – READ
- 1910 – Bechamps vs Pasteur – The Germ Theory – Bechamps had not been heard outside of France – READ
- “It was Bechamp, and not Pasteur, who discovered the cause of fermentation, the cause of the disease of the silkworm and of phyloxera, the disease of the grapevines of France, and also the cause of the coagulation of the blood. He revealed the true functions of the glittering corpuscles, to which he gave the appropriate name ‘microzymas” which in sickness evolve into bacteria. The ordinary definition of microzyma is ‘a microbe or bacteria supposed to act like a fermetn in producing disease.”
1907
1907 – Book: Immunity In Infective Diseases by Elie Metcknifoff (translated from French) (1907) – READ
- Book: The Founders Of Modern Medicine Pasteur. Koch. Lister. by Elie Metcknifoff (1939), first published (1905) – READ, REF
- “Hygiene and prophylaxis were in a rudimentary state. Only antivariolic (small pox) vaccination, worked out by Jenner at the end of the 18th and the beginning of the 19th Centuries, show like a luminous object in the darkness all around.” [clarrifying the “type” of vacci-nation!] – REF
- “A classic example of this is the vaccination of people with the contagious principle of human small-pox — variolation — or with smallpox from a heifer — vaccination.“- REF
- [Note Poliomyelitis epidemic began US ~1907 – REF, was the source of that epidemic from calf lymph? REF]
1906
September 1906 – Annales de l’Institut Pasteur Vol 20 Iss 9: Le microbe de la coqueluche by Bordet and Gengou p. 731 – READ, CREDIT, 1906 “The whooping cough germ”
- Bortet and Gengou were able to isolate the Pertussis bacterium on their special medium.
1904
1904 – A Short Treatise on Anti-Typhoid Inoculation: Containing an exposition of the principles of the method and a summary of the results achieved by its application by Almroth. E. Wright MD (University of Dublin) – READ
- Ch I: On the principles of protective inoculation and the physiology of immunisation – READ
- Machinery of immunisation a chemical machinery. “…the condition of immunity which is achieved appears at first sight to depend upon an exaltation of the power of phagocytes…I have shown…the appearance in the serum of a special class of protective substances – opsonins“…”The machinery of immunisation must…be conceived of as a purely chemical machinery. It is a machinery which elaborated, in response to the appropriate chemical stimulus, the particular internal secretions which is demanded for the purposes of immunisation” – REF
- Observations which show that the typhoid culture preserves its vaccinating efficacy after exposure to temperatures of 6o°-65°C (pg 20) – READ
- The “bactericidal power of the blood is increased — sometimes as much as one-thousandfold — as the result of a single inoculation of a suitable quantum of a sterilised typhoid culture” (Wright Lancet, September 14, 1901)
- Mass cultures of Bacillus Typhosus and Standardisation of the Vaccine (pg 23) and dosage of anti-typhoid vaccine (pg 25) – READ
- “For the present we must content ourselves with the fact that sterilised typhoid cultures have been shown to constitute a vaccine which will induce elaboration of the special varieties of anti-tropins that are required for the protection of the organism against typhoid.”
- “It will presently emerge that the practical efficacy of the vaccine is borne out in a very distinct manner by the statistical records that set forth the results obtained by the actual practice of typhoid inoculation.” – REF [in other words, we’ll know how good it is after mass injections of the stuff]
- Ch III: On the technique of anti-typhoid inoculation and on the clinical symptoms which supervene upon the injection of the vaccine – READ
- “When a suitable quantum of anti-typhoid vaccine, made from a suitable strain of typhoid bacillus, has been injected the local symptoms first make themselves felt after an interval of two or three hours. …In a case where a very toxic vaccine was employed, distinct local effects supervened in a quarter of an hour…”Ch 3 pg 39 – REF
1903
1903 – Special report on the supply of diphtheria antitoxin into the borough, England: READ,
- supplied free of charge for immunisation or treatment of diphtheria or membranous croup
- “By a series of the most careful and exact experiments scientists have now been able to produce an artificial antitoxin or antidote. This antidote is termed diphtheria antitoxin or anti-diphtheritic serum. When injected into the human system in cases of diphtheria it has precisely the same effect as the antitoxin formed in the human system itself, that is to say, it acts as an antidote and counteracts the effects of the toxin produced by the growth of the diphtheria bacillus“
1901
December 1901- First Nobel Prize in Medicine is awarded to E. Behring for antitoxin or serum therapy – TIMELINE
September 14, 1901 – The Lancet Vol 158, Iss 4072, pp 715-723 : On the changes effected by anti-typhoid inoculation in the bactericidal power of the blood, with remarks on the probable significance of these changes, A.E. Wright – READ, CREDIT [Unsure of correct reference]

- The “bactericidal power of the blood is increased — sometimes as much as one-thousandfold — as the result of a single inoculation of a suitable quantum of a sterilised typhoid culture” (Wright Lancet, September 14, 1901) – REF
June 1, 1901 – The Lancet Iss. 4056: A further note on the technique of the quantitative estimation of the bactericidal power of the blood and (incidentally) on the possible application of such estimations on the standardisation of bacterial vaccines (third communication) by Almroth E. Wright – READ
- First communication The Lancet Iss. 4031, Dec, 1, 1900, p1556 : On a method of measuring the bactericidal power of the blood for clinical and experimental uses – READ
- Second communication The Lancet Iss. 4044, Mar. 2, 1901, p609 : On the quantitative estimation of the bactericidal power of the blood – READ
1901 – Neisser & Wechsberg – Showed “bactericidal action of an antiserum in vitro occurs only when bacteria and antiserum have been mixed in optimal proportions” – REF
1901 – Book: Immunity in Infective Diseases by Elie Metchnikoff – French (1901)- READ, translated to English (1905)- READ, CREDIT
The prevention of disease by the production of an acquired immunity is daily assuming greater importance. With the object of arresting the multiplication and dissemination of morbific germs, we are seeking, by artificial means, to render individuals, who may come in contact with them, refractory to their pathogenic action
Elie Metcknikoff
- “This question of immunity is, however, apart from its practical aspect, intimately connected with problems of pure theory. There can be no question that the marked pessimism developed during the century just closed was in a large measure prompted by the dread of disease and premature death, scourges against which humanity is as yet powerless“
1900
(1901-1904) Anti-typhoid bacterial vaccine experiments ramp up by Almroth E. Wright
December 1, 1900: The Lancet Iss. 4031,: On a method of measuring the bactericidal power of the blood for clinical and experimental uses Almroth E. Wright p 1556 (communication 1) – READ, communication 3 – CREDIT
January 20, 1900- BMJ: Remarks on the Results which have been obtained by the antityphoid inoculations and on the method which have been employed in the preparation of the vaccine – A.E. Wright and Major W.B. Leishman (Army Medical School, Netley) – READ
- The method for attaining a “pure and perfectly sterile typhoid vaccine” material – REF
- Antityphoid inoculations were “inaugurated” at Netley in July 1896 with Major D. Semple R.A.M.C, published Jan 1897
1900 – US Deparment of Agriculture (USDA), Division of Entomology gains a new department head, Leland Howard, in September 1895 who is more “progressive” than his deceased predecessor and changes the pest control focus from biological to widespread chemical application starting with the public health topic of mosquito control – TIMELINE, READ
- Howard “promoted insecticides by highlighting a far more pervasive danger: mosquitoes, which had, after the 1900 discovery that they were linked to malaria, become the preeminent pest in America. Concern for the nation’s agricultural prosperity yielded easily to public health anxieties…” REF
1898
Diphtheria Toxin-Antitoxin injections began
1898 – “Earlier in 1898, Behring and F. Wernicke had found that immunity to diphtheria could be produced by the injection into animals of diphtheria toxin neutralized by diphtheria antitoxin.” and so was born the toxin-antitoxin injections. REF
May 1898 – Tri-State Medical Journal and Practitioner: Sudden Death Following an Immunizing Dose of Antitoxin – case report of a 15 year old (pg 239) – READ
- Student of 15 years complaining of a sore throat, he had been exposed to diphtheria. The administered dose of antitoxin “was made between the shouldners and a little to the left of the spine”! He was dead 35 minutes later.
- “Dr. Given Campbell said he did not believe the patient had died from the effects of the diphtheria antitoxin. He thought it might be the effects of psychic shock.” [men of “Medical Science”!]
May 1898 – Tri-State Medical Journal and Practitioner: The Therapeutics of Tetanus (p 241) – READ
- Reports for the past few years place it beyond doubt that the only and the real theraputic means for the treatment of teatanus lies in the [Behring’s] serum treatment. What a God-send is this over the oder and positively uncertain means formally used”
- Heddaeus “believes that preventative serum treatment deserves the best consideration” [meaning to use it as a “vaccine”]
May 1898 – Tri-State Medical Journal and Practitioner: The Patent on Antitoxin – Professor Behring has been granted a patent as the inventor of diphtheria antitoxin – “his claim is an offence to common morality” – (summary of the immunization HISTORY)- READ
- The principles uon which immunization to diphtheria was finally achieved were of gradual growth, the outcome of researches by thousands of untiring workers. The foundation of the workd was undoubtedly laid by Pasteur in his method of immunizing against chicken cholera and anthrax.
- a “contribution to the theory of prophylaxis“
- ‘Emerich and Aronson both dispute the priority of Behring, and the French Academy of Sciences awarded their prize for antitoxin jointly to Behring and Roux”
- “The principle which lies at the foundation of the invention of diphtheria antitoxin, and that which underlies all serum therapeutics, is that the blood of immune animals can be used in the treatment of others.
- …If to any single man must be ascribed the distinction of being the inventor and discoverer of the benefician plinciple of immunization, the honor belongs to the immortal Pasteur“
- Simpson didn’t patent “chloroform anesthesia” nor Lister “antiseptic surgery”
1897
First publication of anti-typhoid Vaccination, and measuring the resulting antibodies
June 5, 1897 – BMJ: Remarks on The Plague Prophylactic Fluid By W. M. Haffkine of Pasteur Instituted – READ, READ2
- June 26 – “The Queen has appointed Dr. W. M. Haffkine a Companion of the Order of the Indian Empire, and this recognition of M. Haffkine’s devoted labours in India for the prevention of cholera and plague by preventive inoculation will cause universal satisfaction.” – READ
March 13, 1897 – BMJ: The extension of the serum treatment of disease – READ
- Within the short space of a few weeks no fewer than three new therapeutic and prophylactic serums have been brought prominently forward, — Yersin’s experiments carried out in China and in Paris, …”quantities quite insufficient to produce antitoxin enough to be of value in the treatment or prophylaxis of bubonic plague,…
- In the meantime Haffkine has tried to utilise the bacilli themselves as a vaccine. Adapting his cholera inoculation method to bubonic plague, he seeks by injecting the dead or partially devitalised bodies of the plague bacillus to produce an active immunity or insusceptibility similar to that described above as occurring in the horse.”
February 13, 1897 – BMJ: Professor Haffkine’s Prophylactic Serum [against the plague bacillus] with which he has had the hardihood to inoculate himself; his statement is as follows – READ He fell ill following this – READ, Haffkine is referenced HERE, anti-choloera inoculation work in India- READ
February 13, 1897 – BMJ: ANTIVACCINATION ‘‘ IN EXTREMIS.” – READ
January 30, 1897 – The British Medical Journal: Remarks on Vaccination against Typhoid Fever – Almroth E. Wright and Major D. Semple – READ, READ This is the inaugural publication of the Antityphoid inoculations conducted at Netley in July 1896 – REF
- Discussed is the purpose of the vaccination and method of preparing the antityphoid vaccines
The object of all vaccination processes is, first, to achieve a degree of immunity which shall be equal or greater to that which accrues to a patient who undergoes and recovers from an actual attack of the disease; and, secondly, to achieve that immunity without any risk to life or health.
Principles upon which the proposed method of typhoid vaccination is based (1897) – REF
- Zooologist, Mr. Waldemar Haffkine “suggested rather more than twelve months ago to one of us that the method of vaccination which has proved so effectual in combating cholera epidemics in India might, mutatis mutandis, be applied also to the prophylaxis of typhoid fever.” (see 1892 and 1894)
- “Owing, in the first instance, to the researches of Pfeiffer on immunity against cholera, and, in the second instance, to the subsequent researches of Gruber and Durham on the differential diagnosis of bacteria by means of the serum of immunised animals [antibodies], we are now in possession of a method which enables us not only to detect the effect that a vaccination exerts on the blood of the patient, put also accurately to measure that effect.” – i.e. detect and measure antibodies
- “These vaccines are made from agar cultures of typhoid bacilli which have been grown for twenty-four hours at blood heat. The cultures which are thus obtained are emulsified by the addition of measured quantities of sterile broth. The resulting emulsion is then drawn up into a series of sterile and duly calibrated glass pipettes. The capillary ends of these pipettes are then sealed up in the flame so as to form vaccine capsules… ”
- “QUESTION OF RISK ASSOCIATED WITH THE ANTITYPHOID VACCINATIONS. “When we appreciate that the bacteria which are employed in these vaccinations are dead bacteria, and that they are incapable of generating new poison in the system, it will be obvious that the injection of small and measured quantities of these dead bacterial cultivations involves no more risk to life or health than the injection of a medicinal dose of morphine, That there is no unknown factor of risk in the case of the injection of bacterial toxines will be evident when we consider that Mr. Haffkine has performed nearly 100,000 anticholera inoculations without a death, and, as far as we can learn, without the supervention of a single serious symptom.” [Wow!]
- It is obvious that a vaccination process has little chance of being widely adopted unless immunity of a more or less durable character can be conferred. A person who submits himself to a vaccination process will always desire to have some guarantee that he will not require to be constantly reinoculated….[duration is unknown] …In the case, for instance, of small-pox, it has always been, and still is, impossible to tell whether a particular patient has lost his immunity and requires to be revaccinated.” [A 100 year old process!]
1896
September 19, 1896 Lancet: On the Association of Serous Haemorrhages with Conditions of Defective Blood-Coagulation by A. E. Wright – READ, CREDIT (Used the word “vaccination” use for Typhoid bacilli)
July 1896 – First inoculation injection of typhoid bacillus into humans and called “vaccination” (see Jan. 30, 1897 above)- REF
- “Our first vaccinations against typhoid were undertaken in the months of July and August [1896]” Wright & Semple (see Jan. 30, 1897 above) – REF
1895
December 19, 1895 – Wood County reporter (newspaper): Conquered at last – effectiveness of antitoxin fully proved, dread of Diphtheria gone – READ, Explore more newspaper articles – SEARCH
- Antitoxin began to be used in Paris in April 1894, and came into general use in September [1894]”.
Johns Hopkins university study July-Aug, 1895 with 7,166 diphtheria cases treated with antitoxin…
October 1, 1895 – Hopkinsville Kentuckian (newspaper): Value of Antitoxin – Some Theories of Natural and Artificial Immunity – READ
- While electricity is taking its place as a motor agent, a new field of usefulness is opening for it…it supplies us with antitoxin – Diphtheria antitoxin introduced into USA December 1894
- Antitoxin is an anti-poison, an antidote for poison”
1894
September 1894, Vol 8 Iss 9: Annales de l’Institut Pasteur: CONTRIBUTION TO THE STUDY OF DIPHTHERIA (Serum Therapy) M.E. Roux and M.L. Martin p. 609 – (French) READ [used Google Translate]
- “Serum therapy has remained on the medical agenda since MM. Behring and Kitasato demonstrated the properties of serum from animals immunized against tetanus and diphtheria…”
- In practice tetanus serum …is still useful in tetanus, but it is not a certain remedy..too late by the time it is employed. [Check translation] Not the case for diphtheria serum…which have been using since 1891 in both animals and children.
- “When serum from an animal immunized against diphtheria [antibody serum] is added to diphtheria toxin, it becomes harmless… We can even inject the toxin first, and, several hours later, the serum; the animal will not perish…” – REF
May 24, 1894 – Zeitschrift fur Hygiene: On the treatment of diphtheria in humans with diphtheria healing serum by H. Kossel pg 489 – with case histories (German) READ
- For 1 1/2 years “I have been researching the use of diphtheria healing serum in children suffering from diphtheria”…when Behring Serum was available in sufficient quantities, I was commissioned by Privy Councilor Koch to work in the sick department of the Institute to start treatment.”
May 24, 1894- Zeitschrift fur Hygiene: About the use of diphtheria antitoxin by P. Ehrlich. and H. Kossel from the Institute for Infectious Diseases in Berlin pg 486 – (German) READ
- “After we had succeeded in obtaining considerable quantities of high-quality serum by immunizing larger animals against diphtheria, we considered it necessary to carry out experiments on as large a number of children as possible according to a uniform plan in order to test its effectiveness on sick people.”…the results were the best in those hospitals in which the largest doses were used.”
- They increased the dose “either by a single injection with a very high effect or by repeated administrations with a lesser effect.”…As far as the total consumption is concerned, we calculate 400 immunization units for mild cases, 1000-1500 immunization units or even more for severe cases.” In Children.
- “Of 55 children, 25 of whom were tracheotomized, 8 died. The deaths belong to certain categories, which we must claim are no longer amenable to therapeutic influence.
May 24, 1894 – Deutsche Medizinische Wochenschrift No 21: On the quantitative determination of diphtheria antitoxin solutions – Behring and O. Boer (pg 453) – READ
- Among the various serum therapeutic tasks that have to be carried out in laboratory work, the numerical determination of the antitoxin value occupies one of the most important positions. We have been working together on this task for years. In the following we want to first give a historical account of the development of the quantitative determination of antitoxins [discovery of specific blood antitoxins,] and then share the experimental results of a value determination using the currently used method. A detailed description of the individual experiments will appear later in the Journal of Hygiene.”
- “The quantitative antitoxin determination for tetanus antitoxin was carried out precisely by Behring and Knorr. In his book “Infection and Disinfection” Behring spoke about this in detail on pages 163 and 164 and in other places.” (Behring-Knorr’s calculation,)
- “For the diphtheria antitoxin, the final development of the same method did not take place until 1893, after Behring and Ehrlich had joined forces to work together. Until then, the valuation of diphtheria was by Von and Wernicke on the one hand, by Behring and Boer, on the other hand, have been carried out from essentially different points of view…”
May 17, 1894 – Deutsche Medizinische Wochenschrift No. 20: On the issue of Diphtheria immunization and healing – Prof Behring and Prof Ehrlich pg 437 – READ
- “We supply the diphtheria antitoxin both a) for immunization and b) for healing exclusively to designated doctors and hospitals.”… [a product they refer to as a “drug”] “Anyone who nevertheless uses our titer for their preparation runs the risk of being unpleasantly disavowed.” The reference Mr. Aronson…
- a) We have not yet identified the antitoxin [antibody serum] dose required for safe, sustained immunization of humans.
March 1894- Antitoxin (antibody serum injections) began to be used in Paris in April 1894 – REF [Actually the newspaper article is incorrect, the use of diphtheria antitoxin serum in humans began in the diphtheria ward of the Institute for Infectious Diseases in Berlin, Germany, in 22 children, from March, April and May 1894 – REF]
March 1894 – Waldemar Mordecai Haffkine, Russian Zooologist , began testing his Cholora “vaccine” on the poor in isolated villages on the outskirts of Calcutta, India – ARTICLE, REF, 2007 – REF,
- Haffkine travelled to India March 1993. He worked with team of Indian doctors and assistants, rather than the British, whom the villages had a distrust. Haffkine publicly injected himself to “prove he thought his preparation was safe”. His field trials using his cholera vaccine inoculations ran from March 1894 to 1896 – REF
1894 – German, Richard Pfeiffer began his studies with cholera infection and immunity which led to a revolution in our conception of acquired immunity from bacteria. – REF Studies on cholera etiology – READ
- “Pfeiffer injected cholera spirilla into the peritoneal cavity of guinea-pigs that had been immunized by means of subcutaneous inoculations of this microorganism. Whereas in the normal peritoneum the spirillum increases rapidly in numbers and leads to a fatal infection, in the immunized peritoneum the vibrios are found to undergo rapid lysis; preparations made at intervals from the peritoneal exudate show increasing numbers of deep-staining granules which finally replace the normal vibrios entirely. Coincidentally with this “bacteriolysis” the animal recovers. Pfeiffer further showed that although his serum obtained from immunized guinea-pigs had in itself no destructive power for the vibrios in vitro, it would, when mixed with them and injected into the peritoneal cavity of normal guinea-pigs lead to the specific form of lysis.”
1893
Haffkine develops first bacterial disease vaccine – anti-cholera vaccine
April 27, 1893 -Deutsche Medizinische Wochenschrift (German Medical Weekly) : For the treatment of diphtheria sufferers with diphtheria healing serum – Behring, Boer and Kossel – (2 parts) No 17 – READ, and May 4, 1893 No 18 – READ, REF
February 11, 1893 – The Lancet: Injections Against Cholera: A Lecture by M. Haffkine p 316 – READ, CREDIT, Haffkine’s paper had to be translated into English, read by Dr Ruffer.
CLICK to see notes
- While visiting, “Haffkine…made some demonstrations at Netley Hospital of his method of inoculating a modifed cholera virus as a protective against cholera [and ] invited to give at the Laboratories of the Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons a demonstration of his method of procedure”
“The discovery that microbes may change their characters and are capable of transformation by artificial means into vaccines of fixed and ascertained power is without doubt the greatest step which has been taken in medical science since disease-producing microbes were first studied. The task which then presented itself to investigators was that of discovering the germs of contagion which were recognised as being the cause of disease and of elaborating substances protective against them
Opening paragraph of Haffkine’s lecture on Injections Against Cholera (1893)
- “The acquisition of virus [poison] of this kind and the establishment of a method suitable for keeping it in a fixed state are the ultimate aims of the research for a vaccine, since it is essential gradually to accustom the organism under treatment to this fixed virus.”
- [From this statement it appears clear at this time in history that the use of the word “vaccine” refers to the prepared product, a “fixed virus”, that would be used to inoculate.]
- “It is known that this task may be accomplished by the transference of infective organisms through a series of animals and that it is by cultivating it through a long series of such living animals that the microbe acquires the maximum of its infective power.” i.e. maximum virulance. [The original Gain of Function experiments, passage through animals, to gain something stronger than naturally occurs]
- For the Cholera bacterium they choose to passage it through the peritoneal cavity of animals, exposing the “discharge’ to air , then transferring that “discharge” to the next animal!…”The virus when injected under the skin of a healthy animal gives the creature, after several days, immunity from the poison of cholera,…” The wound is alarming so can’t be applied to man!
- “Besides, although it does not in itself present any danger to the health of the individual [!!!], it subjects him to all the dangers arising from an open wound…” [I can see this leading to injection into the muscle to hide this “open wound”]
- “Thus the method of inoculation deals with two vaccines—a mild one obtained by weakening the ‘fixed virus,’ and a ‘strengthened vaccine’ which is really the exalted virus itself. The reason an ordinary virus is not used to obtain the weakened vaccine,… is that the viruses in their natural state, especially when they have reached a saprophytic stage of development, present such great differences that there is no certainty in their application.” [The pathogens naturally attenuate, and cause no/mild disease?]
- “Thus in taking vaccine for use as vaccine lymph from a subject slightly affected a very weak substance was sometimes obtained incapable of causing protection, but still able to kill individuals less resistant. ‘The great point of Jenner’s discovery lay in the fact that it indicated a substance fixed by successive passages through animals at a virulence above that which is fatal to human beings. [justifying smallpox inoculation failure!!]
- M. Haffkine was the first to be inoculated with his own virus. He has undergone the operation three times…
- First Dose: “In all cases the method has proved to be absolutely harmless to health. The symptoms consisted merely of a rise of temperature, a local sensitiveness at the place of inoculation and the formation of a temporary swelling at the same place….”
- Second Dose: The symptoms following the second inoculation are usually more marked but of shorter duration; the whole giving rise to a feeling as of a bad cold in the head, lasting from one to two days. The microbes which are introduced under the skin do not propagate, but die and disappear after a certain time.”
- “It is found that the same result can be obtained if the microbes be killed before inoculation. Thus vaccines have been preserved in weak solutions of carbolic acid in which the microbes die at the end of several hours, and the vaccine preserved in this way has been found to be still efficacious six months after its preparation.
- …the absence of living germs makes the vaccines perfectly safe.“
February 4, 1893 – British Medical Journal: On Haffkine’s method of vaccination against Asiatic cholera. Wright AE, Bruce D, pg 227–31 –READ [written immediately after Haffkine’s visit to Britain]
1892
Haffkine develops first bacterial disease vaccine – anti-cholera vaccine
1892 (in the lab) – Journal of Medical Biography: Waldemar Mordecai Haffkine, CIE (1860-1930): prophylactic vaccination against cholera and bubonic plague in British India by Hawgood (2007) – READ, History – PDF
- “Haffkine had developed an anti-cholera vaccine at the Pasteur Institute, Paris, in 1892. From the results of field trials in India from 1893 to 1896, he has been credited as having carried out the first effective prophylactic vaccination for a bacterial disease in man. When the plague pandemic reached Bombay, Haffkine became bacteriologist to the Government of (British) India (1896-1915)…In 1902 19 people in Mulkowal (Punjab) died from tetanus poisoning as a consequence of antiplague vaccination” developed by Haffkine, he was “exonerated only in 1907”. Indian Institutes were named after Haffkine – REF
- Pierre Roux (1853–1933) brought Haffkine into the laboratory of microbial technique where he took part in preparing the course in general bacteriology that Roux and Metchnikoff had initiated.
1892 – Zeitschrift fur Hygiene (Hygiene magazine): On the treatment of diphtheria-infected guinea pigs with chemical preparations by Oscar Boer pg 154 – READ
- “Behring’s experiments proved that guinea pigs, which, according to other experiences, die of typical guinea pig diphtheria within 30 hours at the latest without treatment after infection with diphtheria bacilli, can be saved with great certainty if local treatment is given immediately after infection is carried out with iodine trichloride solutions….However, this treatment has a number of undesirable side effects..”
- “I call the sublimate, the mercury oxyeyanide, sublimate with added lithium chloride; then the gold sodium chloride and the gold potassium cyanide; silver nitrate, carbolic acid, cresol in soap solution, creolin, lysol, naphthylamine, cumene; also the methyl violet, which Stilling called pyoctanin, and the malachite green.” [no wonder the old school doctors looked favourable on antitoxin serums..]
1891
1891 – In 1891 first child treated, the 1892 he started the first human trials of the diphtheria antitoxin, but they were unsuccessful. Successful treatment started in 1894, after the production and quantification of antitoxin had been optimized – REF
1890
They use a lot of guinea pigs in animal experiments! Behring and Kitasato discover Diphtheria bacteria and Tetanus bacteria secrete a toxin – the property which causes the disease
1890 – The Homoeopathic Publishing Co,: Five Years’ Experience in the New Cure of Consumption – READ, PDF, The Homeopathic Recorder – comparing Burnett’s cure to Koch – CREDIT
- “The difference between Dr. Burnett’s Bacillinum and Koch’s “Lymph“ is this: the former is the virus of the disease itself while the latter is the same virus artificially obtained in an incubator by means of heat and beef jelly. Both proved their remedies. Dr. Burnett, on himself, in the regular Homoeopathic way and Dr. Koch by a subcutaneous injection on himself…
- Dr. Burnett’s remedy has to all appearances cured a great many cases of what were, to all appearances, well marked consumption.
- Dr. Koch’s remedy has not cured a single case of consumption. Dr. Burnett’s remedy has harmed no one, while Dr. Koch’s is suspected of having caused the death of scores.” – READ
December 11, 1890 – Deutsche Medizinische Wochenschrift no 50: Investigations into the development of diphtheria immunity in animals Dr. Behring p1145 (German) – READ
- Diphtheria culture was grown in broth with iodine trichloride
December 4, 1890 – Deutsche Medizinische Wochenschrift (German Medical Weekly) no 49: Ueber das Zustandekommen der Diphtherie-Immunität und der Tetanus-Immunität bei Thieren (On the development of diphtheria immunity and tetanus immunity animals) Dr. E. Behring and Dr. S. Kitasato p1113 (German) – READ, READ
- “In our studies on diphtheria (Behring) and tetanus (Kitasato), which have been ongoing for a long time, we have also approached the therapeutic and immunization questions, and with both infectious diseases we have succeeded in curing infected animals as well as in pre-treating healthy ones that she no longer suffers from diphtheria or suffer from tetanus.”
- It “is necessary to prove the correctness of the following sentence: “The immunity of rabbits and mice that are immunized against tetanus is based on the ability of the cell-free blood fluid to render harmless the toxic substances produced by the tetanus bacilli.” – conducted mouse experiments with a control
- “In 1890 Behring and S. Kitasato published their discovery that graduated doses of sterilised broth cultures of diphtheria or of tetanus bacilli caused the animals to produce, in their blood, substances which could neutralize the toxins which these bacilli produced (antitoxins). They also showed that the antitoxins thus produced by one animal could immunize another animal and that it could cure an animal actually showing symptoms of diphtheria.” – REF, REF2
- They also found “that by treatment with certain chemical substances the toxins of diphtheria and of tetanus could be weakened so as to be better supported by laboratory animals; animals treated with these, weakened toxins became immune from doses of the whole toxin that were fatal to the normal animal. – REF
- “It was work on toxin-induced immunity which lead to the demonstration by von Behring and Kitasato in 1890 that immunity to tetanus follows injection of tetanus toxin was the result of the appearance of a ‘factor’ in the serum which neutralized the toxin. This anti-toxin activity could be transferred to normal animans by injecting serum from immune animals. It thus appeared that the body is able to respond to infectious organisms or injurous substances by producing serum components which would combine with these ganets and neutralize their effects. These components were thus called ‘antibodies‘ and the agents provoking their production were termed ‘antigens‘.” – REF
- [From here, until mid 1900s the terms antitoxin, serum therapy, antiserum, sera all refer to antibody products used for “immunizing”, “immunizing treatments” and likely other terms – it’s very confusing.]
1890 – Zeitschrift für Hygiene : About antibacterial properties of different types of blood serum. A contribution to the immunity question. by Von Behring and F. Nissen, p 412 – READ, CREDIT
- “They demonstrated that the blood-serum of guinea-pigs that had been immunized against the Vibrio metchnikovi, would kill these micro-organisms better in vitro than would the serum of normal guinea-pigs.” – REF
November 1, 1890 – Deutsche Medizinische Wochenschrift: I. Weitere Mittheilungen über ein Heilmittel gegen Tuberculose (I. Further information about a cure for tuberculosis) – Robert Koch (German) – READ, PDF, CREDIT
August 1890 – At a press confrence Robert Koch dramatically announced that he had discovered a cure for tuberculosis – the miracle substance was subsequently revealed to be tuberculin, inoculated as a ‘vaccine therapy‘ – REF, CREDIT
- Because of Koch’s reputation, the “vaccine therapy” was quickly taken up by physicians around the world. In a study that followed “it was found patients who received it were more likely to die than recover and that there were many cases of their infection rapidly progressing” – REF Koch’s reputation was grievously damaged
1890 – “Contribution to the study of acquired immunity.” Roger – (translated from German/French) REF
- “Vaccination [La vaccination] causes chemical modifications in the body which make the humors and tissues unfavorable to the growth of the microbe, against which the animal has been protected.”
- [The term “vaccination” used in reference to inoculation other than with cowpox.]
1889
1889 – Kitasato succeeded in obtaining a pure culture of the Tetanus bacillus – REF
1888
Roux and Yesin are the first to demonstrate Diphtheria bacteria secrete a poisonous substance, and is the cause of the diphtheria Disease
1888 – The word “toxin” was coined in 1888 by Ludwig Brieger to qualify different types of poison released by bacteria. – REF
December 1888 – Annales de l’Institut Pasteur: CONTRIBUTION A L’ETUDE DE LA DIPHTHERIE (Contribution to the Study of Diphtheria) | Vol 2, Iss 12, by Émile Roux and Alexandre Yersin, pg 629 – READ, CREDIT
- Roux and Yerson were the first to find in filtered cultures of the diphtheria bacillus a substance that was fatal for guinea-pigs in very small doses. – REF, REF
- Roux and Yersin were “medical doctors at the Institut Pasteur in Paris, took another big step when they showed that a substance secreted by the bacteria was the particular culprit. In the lab, researchers grew the bacteria bathed in a broth; after siphoning off the fluid and filtering it to remove any cells, Roux and Yersin found that the fluid contained a potent toxin. Small doses of the diphtheria toxin could do great damage in susceptible animals. So the scientists mixed the toxin with an iodine solution, which made it far less deadly.” – REF
1887
1887 – In 1887 Roux and Chamberland immunized animals against malignant edema with sterilized anthrax cultures – REF
1887 – Sewall immunized pigeons against the poison of rattlesnakes – REF
1886
“bacterium coli commune” is published by Theodor Escherich (the bacterium today is knowns as Escherichia coli)
1886 – Die Darmbakterien des Säuglings und ihre Beziehungen zur Physiologie der Verdauung (1886) by Theodor Escherich – READ, WIKI
- It was also the publication where Escherich described a bacterium which he called “bacterium coli commune”, the common colon bacillus now known as Escherichia coli. – (German) READ, REF
- Theodor Escherich: The First Pediatric Infectious Diseases Physician? (2007) – READ
1885
Pasteur’s develops Rabies (Hydorphobia) inoculation treatment – Disease Prevention by Inoculation using animal passage to increase virus virulance, before attenuating it with Dry, sterile air.
December 25, 1885 – Buffalo Med Surg J.: Hydrophobia and Pasteur’s Experiments – READ, PDF
- The “prevention and cure” of Hydrophobia or Rabies is claimed. But the “validity of these “cures” must, of course, be left to the test of time”! – REF
- Since the dog that bit Joseph Mister was immediately killed it was not certain if it had Rabies
Already he has won the veneration of our profession by demonstrating that Jenner’s great discovery of vaccination was not an isolated and empirical fact, but that it was only a single member of a united family held together by the great scientific law, that disease may be abbreviated or prevented by the inoculation of a modified or attenuated virus of the same.
Medical Sciences “great scientific law” – READ [virus means “poison”]
- Pastuer’s “method of attenuation is to transmit hydrophobia from rabbit to rabbit by intracranial inoculation, until, after some fifteen transmissions, [or up to 25 times] the shortest period of incubation and the greatest degree of virulence have been attained. Then the spinal cord is taken from an animal dead of the disease, and it is suspended in a perfectly dry tube. Here it is kept, and the virulence of the poison is found to gradually diminish, until it at last disappears on about the fifteenth day…”
- This same “atenuation process” was followed by Haffkine 1893 for anticholera inoculation develpment – REF
October 31, 1885 -Daily Evening Bulletin Kentucky: No more hydrophobia: Dr Louis Pasteur’s cure for the mad dog’s bite – READ, CREDIT, REF , The Daily Globe – READ Pasteurs Rabies experiments began November 1882 – REF
- RE M. Louis Pasteur’s paper read in the French Academy of Sciences on October 26, 1885. by December 27, 1885 is translated into English – READ
CLICK to read how Pasteur prepared his inoculum and tested on first human:
At perhaps the most important sitting held by the academy of sciences Dr Pasteur thus described the process of cure by means of a rabbit inoculated with the fragment of a tissue taken from the spine of a rabid dog. The incubation of the poison occupied fifteen days. As soon as the first rabbit inoculated was dead a portion from its spinal marrow was in turn inoculated into a second rabbit, and so on until sixty rabbits had been inoculated, At each successive inoculation the virus increased in potency, and the last period of inoculation did not occupy more than seven days.
Having ascertained that exposure to dried air diminished the virus, and consequently reduced its force, Dr Pasteur supplied himself with a series of bottles of dried air. In these bottles he placed portions of inoculated spinal marrow at successive dates, the oldest being the lease virulent and the latest the most so.
For an operation Dr Pasteur begins by inoculation his subject with the oldest tissue, and finished by the injection of a piece of tissue whose bottling dates back only two days, and who’s period of inoculation would not exceed one week. The subject is then found to be absolutely proo against the disease.
Newspaper describing Pasteur’s successive inoculation process
- A 12 year old boy named Joseph Meister becomes the first human treated using Pasteur’s new method of vaccination. Meister had been bitten multiple times by a rabid dog, and his doctors concluded he was “doomed to a painful death” and thus he “might be experimented upon”. Inoculations started 60 hour after first being bitten. [REF]
In thirteen days inoculations were made upon Meister with pieces of spinal marrow containing virus of constantly increasing strength, the last being from the spine of a rabbit that died only the day before. Now a hundred days have passed since Meister underwent the last inoculation. The treatment has been thoroughly successful and the boy is in perfect health.
- Pasteur suggested an establishment where rabbits will be kept inoculated with the rabies disease to ensure a “constant supply of spinal tissue of old and recent inoculation would always be ready” [keeping rabbits in a constant state of hell]
- The primal causes of hydrophobia were unknown at the time, yet Pasteur “emphatically stated that the cure for hydrophobia had been found.”
“…the malady is transmissible only by bite. If, therefore, by a general compulsory inoculation of dogs for several generations dogs had been made incapable of hydrophobia, the malady would have disappeared and there would be no occasion to ask whether inoculation had a permanent effect or not.Pasteur stated
- Pasteur was not commonly known in Americans at the time. His saving of the silk worm industry helped France pay reparations back to Germany faster! – READ
- The process is commonly called “inoculation” [not vaccination”
…inoculation is not limited to human beings. It was really by inoculation of silk worms that Pasteur saved our sick industry from the destruction that threatened it years ago.
Dr Grancher speaking on behalf of M. Pasteur
- The Principle of Pasteur’s Treatment of Hydrophobia in brief:
“Pasteur’s treatment of hydrophobia consists in producing, during the period of incubation of the disease, and artificial immunity in the person bitten by a radid animal. This is accomplished by inoculation the individual on successive days with virus of different degrees of activity, commencing with a very attenuated virus and using on each succeeding day a virus of greater intensity”
1891
1885 – The Pasteur Institute was established, funded by the manufacture of Pasteur’s animal anthrax vaccine (chemically treated not attenuated by exposing to air??) – REF
1885 – Modern Medicine (1913) Tetanus pathogen is discovered (or first published) by Nicolaier – READ Just Notes:
- In 1885, Nicolaier discovered the Bacillus tetani. It is a long, slender rod, one end of which is often occupied by a spore; this distends the cell into a pin or “drumstick” shape… Kitasato was the first to make pure cultures; this is difficult, since the presence of the smallest amount of oxygen interferes with their growth… The bacilli can be isolated from the wound in which they develop, but do not enter the circulating blood…
- Brieger has obtained two poisons from sterilized pure cultures, terming the one “tetanin” and the other “tetano-toxin,” both being virulent poisons. These alkaloidal substances cause the tonic spasms, so that tetanus is classed as an intoxication.
- Immunity: Behring and Kitasato have produced artificial immunity in animals by the inoculation of cultures of the tetanus bacillus after the addition of iodine trichloride to diminish their strength.”
- The use of “antitoxin” is noted as a “treatment”
1884
Diphtheria bacillus discovered by Klebs and Loeffler, Tetanus bacillus discovered by Nicolaier, Typhoid bacillus isolated by Gaffky
1884? – Fredrick Loeffler, a German bacteriologist, took the diphtheria microbe which Prussian pathologist Edwin Klebs found in 1883, blocking airways of patients with diphtheria. Loeffler grew it in the lab, and using “Koch’s Postulates” demonstrated the pathogen was the cause of the diphtheria disease. The bacterium came to be known as the Klebs-Loeffler bacillus (later, Corynebacterium diphtheriae). – REF
- Freidrich Loeffler (1884), and Emile Roux and Alexandre Yersin (1889) noted the presence of virulent diphtheria bacilli in the throats of healthy individuals, as well as the persistence of infecting organisms during convalescence. …It was in connection with the cholera epidemic of 1892 and 1893 that the significance of the human carrier was first realised. – REF
1883
Cholera Bacillus discovered by Koch
1883 – Robert Koch (1843–1910) had shown the bacterium Vibrio cholerae to be the causative agent of Asiatic cholera. – REF
1882
Metchnikoff’s phagocytic theory of immunity
November 1882 – Pasteur begins his Rabies inoculation experiments in dogs and rabbits. He presents his results Oct 1885 – REF
May 1, 1882 – Pall Mall Gazette: Chinese immunity from disease READ, why were Chinese allegedly less impacted from disease? Ancient Chinese medicine?
1882 – In 1882 Elie Metchnikoff “began recording his observations on the function of the white blood corpuscles in protecting the body from disease,…Metchnikoff was able to show that the outcome of the infection depends entirely on the completeness with which the blastomyces is engulfed by the leukocytes of the host. He was soon after able to demonstrate that frogs and mammals also combat experimental bacterial infection by a similar process of phagocytosis.” –REF, pg 519 READ
- Immunity in Infective Diseases by Elie Metchnikoff – English (1905)- READ, French (1901)- READ
- “Metchnikoff (1882) produced evidence …to support the view that phagocytosis (‘cellular eating’) of microorganisms by leucocytes was the major host defence against infection. His views were bitterly opposed by the proponents of the antibody (humoral) hypothesis of host protection.” It would not be until 1903 when Sir Almroth Wright “showed that antibodies actually aided the phagocytosis of bacteria” Wright called this opsomization – ” Thus both cells (phagocytes) and antibodies were shown “necessary for an effective host response to infection.” – REF
1882 – London Society for the Abolition of Compulsory Vaccination: Testimonies of Medical Authorities on Vaccination. With index, distinguishing by an aserisk such as treat of animal lymph (cow, horse, or calf), without reference to arm to arm vaccination – READ, The societies paper The Vaccination Inquirer (1880) – EXAMPLE, more publications – SEARCH
- “The opposition to compulsory vaccination is based mainly upon two propositions:
- First, that vaccination, which was claimed by Jenner and his immediate followers to afford immunity from small-pox for life, does not afford immunity either for life, or for any portion of life, and
- secondly, that the operation is always attended with danger, and is sometimes fatal.”
- “These testimonies demonstrate that the failures of vaccination to protect were coincident with the introduction of the Jennerian rite, and it is no longer denied that numerous cases of small-pox were discovered amongst patients who had received virus from Jenner’s own lancet”…- REF
1881
Louis Pasteur introduced the concept of “attenuating the virulence” of organisms so that they could be used as live vaccines. Did he commit fraud?
October 12, 1881 -Second International Anti-Vaccination Congress: Sanitation, Not Vaccination, The True Protection against Small-Pox – READ
- “…Leicester Free Press, it is said : — ” So far as we are concerned in Leicester, a town containing 120,000 inhabitants, with many thousands of unvaccinated children, smallpox seems to be about the least dangerous of all diseases, and is not to be named by the side of scarlet fever, measles, whooping cough, diarrhcea, or even consumption. If a case of small-pox is discovered, instant isolation is adopted, and during the last five years we have hardly had five deaths. That being the state of the case, one need not wonder that the fear of the disease should disappear, or that resistance to vaccination should increase.” [Leicester abolished compulsory vaccination] – REF
May 5, 1881 – Pasteur’s demonstrated his Anthrax vaccine on sheep at Pouilly-le-Fort from May 5-31, 1881 – WIKI
- At Pouilly-le-Fort, Pasteur used a vaccine attenuated by potassium dichromate, employing a process similar to Jean Joseph Henri Toussaint’s, who had published a means of attenuation by another antiseptic, carbolic acid. Pasteur never gave proper credit to Toussaint and his discovery. [unsure year of Toussaint’s work]
March 21, 1881 – Pasteur reported testing his vaccine in sheep was superior to Toussaint‘s work – READ, CREDIT
- The Private Science of Louis Pasteur. Princeton by Geison GL. (1995) – READ
- Pasteur received credit for developing the first successful vaccine against anthrax. “Toussaint subsequently published only 2 more scientific papers before he died in 1890 at the age of 43, after suffering a mental breakdown.
- It was not until 1998, that the French government officially recognized Toussaint’s vaccine as the first effective vaccine against anthrax.” – REF
- Toussaint use an “old method of inoculation against anthrax…the first of its kind, which has had to give way to the method of M. Pasteur. simply because Pasteur’s method was based upon a virus of fixed strength and produced results with certainty, conditions which were wanting in the former method.” –REF
- “It is noteworthy that Robert Koch, who became one of Pasteur’s chief competitors, hailed Toussaint as the worthy inventor of vaccination against anthrax, and persistently denigrated Pasteur’s contributions to microbiology” – REF
February 28, 1881 – Comptes Rendus des Seances de L’Academie des Sciences | Vol 92, Iss 9: De l’attenuation des virus et de leur retore a la virulence (On the attenuation of viruses and their return to virulence) by L. Pastuer with Chamberland & Roux, pg 429-435 – READ, CREDIT where virus means poison in Latin
- “In this publication, Pasteur claimed that he could attenuate the anthrax organism by simply culturing it in air at elevated temperatures” – REF
- Pasteur “thus introduced the concept of attenuating the virulence of organisms so that they could be used as live vaccines. Audaciously, he speculated that all microbial diseases could be prevented this way: one only had to learn how to culture the offending agent. Of course we now know that it is not quite as simple as Pasteur originally claimed, particularly for bacterial infections.”
- “The first inoculation of twenty-four sheep, one goat and six cows with an attenuated anthrax culture took place on the 5th of May, 1881″ – REF
- “Louis Pasteur first proposed that the solution to infectious diseases was to culture the microbes and attenuate their virulence, so as to use them as vaccines.” – REF
- The “vaccine introduced by Pasteur in 1881 was in fact not the live attenuated vaccine that Pasteur had suggested he used at the time. Instead, the vaccine was a chemically killed vaccine that had been developed and introduced by one of Pasteur’s rivals, a Dr. Toussaint, who was a veterinarian from Toulouse, France.” – REF
- “Pasteur did not announce the discovery of his own “live attenuated” anthrax vaccine until February 28, 1881. Of significance, Pasteur linked his new vaccine with his earlier chicken cholera vaccine by ascribing attenuation in both cases to the action of atmospheric oxygen. However, there was an important difference between the production methods of the two vaccines. Unlike the chicken cholera microbe, the anthrax bacillus formed spores that “resisted the attenuating effects of atmospheric oxygen”” – REF
1880
Pasteur’s application of inoculation with an attenuated bacteria, and demonstrating resistance to formation of disease following challenge with new culture – Ushers in of the Golden Age of Bacteriology
Not quite 100 years since being coined by Jenner, the term “Vaccination” is no longer reserved for smallpox inoculation (vaccina-(inoculA)tion) – the use of the term in literature from here on becomes confusing.
December 1880 – The first International Anti-Vaccination Congress was held – REF
1880 – A History of Public Health – The golden age of bacteriology is ushered in with the discovery of pathogens linked to disease and the desire to control them. [beginning more 1870] – REF
- Pasteur observed “that virulence of pathogenic microbes could be modified under various conditions. Thus, between 1880 and 1888, Pasteur began to investigate the modification of virulence in disease-producing germs. Following the lead provided by Jennerian vaccination, he conceived the idea of preventing infectious diseases by means of vaccines prepared from such attenuated strains. Of the greatest import were the results of Pasteur’s work on chicken cholera, swine erysipelas, and rabies, researches that led to the development of immunology and that were to have a profound and practical impact on the creation of a scientific public health program at the beginning of the twentieth century” – REF
- The term “vaccine” no longer solely attributed to vacca, and vaccines inextricably linked to “public health”.
- Extending from this period:
- The work of Koch “led to the development of technical methods for the cultivation and study of bacteria” so as to obtain pure cultures. – REF
- Where as Pasteur’s work turned attention to “the mechanisms of infection” and the development of the “prevention and treatment of contagious disease”. Pasteur refocused the term “vaccine” and “vaccination” to be applied to all pathogens not just variola vaccinia, from where the term is derived. – REF

August 1880 – “the question of “live vs. dead” vaccines.”In August, 1880, soon after announcing his heat killing method of vaccine production, Toussaint switched his procedures and had begun to subject the bacilli to the action of carbolic acid, which had long been used as a disinfectant and had more recently become famous as Joseph Lister’s “antiseptic” of choice for the treatment of surgical wounds.” – REF
July 12, 1880 – Toussiant’s result of his attenuated vaccine against anthrax are presented to the French Academy of Sciences – he reduced virulance by a chemical manner using carbolic acid. – REF, WIKI
CLICK history notes on Toussiant
- “Henri Bouley (a fellow veterinarian and friend of Toussaint) read before the Academy of Sciences a report from Toussaint (who was not a member of the Academy), which described the initial results of his experimental vaccine trials, [with chemical attenuation]. In contrast to Pasteur’s “live attenuated” vaccine, Toussaint generated his vaccine simply by killing the bacilli by heating for 10 minutes at 55°C.”. …- REF
- “In August, 1880, soon after announcing his heat killing method of vaccine production, Toussaint switched his procedures and had begun to subject the bacilli to the action of carbolic acid, which had long been used as a disinfectant and had more recently become famous as Joseph Lister’s “antiseptic” of choice for the treatment of surgical wounds.” – REF [this timestamp needs checking]
- Toussaint does not get the credit for chemical attenuation (until 1997!), he dies of neurologic illness in 1890 – REF
- In 1879 Toussaint, who admires Pasteur “finds first and isolates the microbe of “cholera des poules” [Chicken cholera] (now Pasteurella) and gives Pasteur this new germ which will be used by Pasteur for his particular works about reducing of virulence by successive subcultures.” – REF
February1880 – Recueil de Médecine Vétérinaire Année Vol 57: On virulent diseases, and in particular on the disease commonly called chicken cholera. Pasteur L., pp. 125-135 – PDF, READ vaccine for chicken cholera
CLICK notes on chicken cholera
- “… the first example of attenuation of a virus using experimental resources alone.”
- “The practices of vaccination and variolization have been known in India for the longest time. Even before Jenner demonstrated the efficacy of vaccinia, people of the countryside where he practised already knew that cowpox protected against smallpox. The facts about vaccinia are unique, but the facts about non-recurrance of virulent diseases are more general. The organism never expresses twice the effect of chicken pox, scarlet fever, typhus, plague, smallpox, syphilis and others, as the immunity lasts for a long time at least.” – REF [ for natural infection]
- Pasteur then introduced the problem of chicken cholera, and mentioned that M. Toussaint, a professor at the veterinary school of Toulouse…” Pasteur claimed he had discovered a “diminish the microbe’s virulence by changing the mode of culturing.”With this presentation to the Academy, Pasteur merged the science of microbiology with that of what subsequently became known as immunology for the first time”….Pasteur thus kept it a secret as to exactly how he had attenuated the virulence of the chicken cholera microbe for more than 9 months, until October of 1880…Eventually, Pasteur disclosed that his methods simply involved culturing the microbe exposed to atmospheric oxygen for prolonged intervals, i.e. longer than 2–3 months. However, he never explained why oxygen should weaken the microbe’s virulence,…”. – REF
- “It seems as if the initial microbe inoculations (of the live attenuated vaccine) have depleted a certain element that healing does not reconstitute and that the absence of which hinders the development of this small organism (when re-inoculated a second, third, and fourth time). This explanation will without doubt, become general and applied to all infectious diseases.”
- Pasteur showed bacterial “culture could be attenuated into mildness. So he inoculated the birds with the mild culture, then with the powerful, virulent new cultures — and all the chickens recovered. Having resisted the mild attack, they had become immune to the deadly one.” He repeated this process with other animals – REF
- Thus, the host would not support the growth of a subsequent infection by the virulent microbe, and would be “immune” (Latin, immunis; free, exempt).” …central to Pasteur’s conception of immunity, was the biological activity of a living, if attenuated, microbe that depleted the host of essential nutrients. It was Toussaint’s claim that he had in fact produced a “dead” vaccine against anthrax that moved Pasteur to state that “it overturns all the ideas I had on viruses, vaccines, etc.”…the question of “live vs. dead” vaccines.– REF
1878
Germ Theory of Disease
1878 – Comptes Rendus Hebdomadaires des Seances de l’ Academie des Sciences | Vol 86: La theorie des germes et ses applications a la medicine et a la chirurgie. (Germ theory and its applications to medicine and surgery) L Pasteur, C Chamberland, J Joubert, pp 1037–1043 – READ, CREDIT
- in April of 1878, just two years after Koch’s revolutionary publication proving the microbiological cause of anthrax, Pasteur presented a “Summary” to the Academy of Sciences, essentially claiming priority of the germ theory of disease … Koch had already demonstrated the culture of the anthrax microbe two years earlier.- REF
1877
July 16, 1877 – Weekly reports of the sessions of the Academy of Sciences: Physiological Chemistry – Anthrax and septicemia. Note from Pasteur and Mr Joubert (French) – READ, READ, CREDIT
- Re previous meetings from April 30, 1877. “To rule out any hypothesis of the simultaneous existence of a virulent material associated with the bacteridia in the anthrax blood,… In summary, anthrax must be called today the disease of bacteridia…” either in the “form of filaments or that of corpuscles”.
- ““At a local slaughterhouse, [Pasteur] obtained anthrax-infested blood from the carcasses of a horse, a sheep and a cow,” Lehrer writes. That blood formed part of the basis of a paper he published in a French science journal about a month later—the beginning of research into anthrax that would be important to developing the first vaccine for anthrax” – REF
1876
Anthrax, the first disease proven to be caused by a microbe, by Robert Koch
1876 – Beitrage zur Biologie der Pflanzen Vol 2: Die aetiologie der milzbrand-krankheit, begrundet auf die entwicklungsgeschichte des bacillus antracis (The aetiology of anthrax disease, based on the evolutionary history of Bacillus antracis) Koch R., pp 277–310 (German) – READ, CREDIT
- Anthrax was the first disease proven through experimentation to be caused by a microbe by Robert Koch, making “anthrax central to the history of medicine”. – REF
- Koch “was the first to succeed in changing the thread-like microscopical corpuscles identified by others (in France) into identifiable filaments (chains of rods) and then into beads consisting of minute grains, the spores. This great discovery of the spore of anthrax removed all doubts regarding the role of bacteria in the causation of anthrax, for it illuminated all points hitherto left unexplained.” – REF
- With this finding “medical bacteriology was ready to be born” – REF
1868
October 19, 1868 – Louis Pasteur was “struck by cerebral congestion” and remained partially paralysed as a consequence – REF, READ, CREDIT (Google translated)

Major Medical Problems ( Les Grande Problemes Medicaux) – concerning the History of so-called organisms (French) the evolution of Bechamp’s own research – READ
- On March 21,1869 Pasteur claimed to have been researching silk worm for the “past 5 years” to “discover a preventative means for the disease which decimates silkworms” [which would make it c. 1863 or 1864]
- But according to (Comptes Rendus, t. LXI, p. 506) Pasteur noted arriving in Alais on June 7, 1865 “to take care of the pebrine“, which is when his work on silkworms would have begun –REF
- Prof Bechamp declared “Pasteur’s illness was the consequence of panic, following the disappointment of not having succeeded, in 1868, to investigate the disclosure of his plagiarisms and deceptions” – REF
1867
September 21, 1867 – BMJ: On the antiseptic principle in the practice of surgery. Joseph Lister Vol 2 pg 246 – READ, CREDIT
- The founding of “antiseptic medicine” was credited to surgeon Sir Joseph Lister, not Semmelweis who proposed washing hands with chlorinated lime solutions between visiting patients, a major conflict with the medical establishments way of thinking! – TIMELINE
- In 1864, while working at Glasgow University as Professor of Surgery, Jospeh Lister was introduced to Pasteur’s germ theory of disease, and decided to apply it to the problem of surgical infections.” – READ
- The “antiseptic principle“, as Lister termed it, was first applied on August 12, 1865, and his report of the results appeared in the Lancet between March and July 1867.” Acceptance of Lister’s “technique and the principle underlying it was neither rapid nor widespread” – REF
1857
1857 – Comptes Rendus des Seances de L’Academie des Sciences | Vo 45: Memoire sur la fermentation appelee lactique. (ORGANIC CHEMISTRY. — Memoir on fermentation called lactic acid) – Pasteur L., pp. 913–916 – READ, CREDIT
- “Louis Pasteur’s demonstration in 1857 that fermentation of lactic acid into alcohol and carbon dioxide was actually caused by living organisms (animal infusoria), and not by the then popular theory of “spontaneous generation”, set the stage for the importance of microbes in everyday processes” – REF
- “It takes very little of this yeast to transform a lot of sugar. These fermentations must preferably be carried out sheltered from air, otherwise they are hampered by vegetation or parasitic infusoria…”Lactic fermentation is therefore, as well as ordinary alcoholic fermentation, a correlative act of the production of a nitrogenous material which has all the appearance of an organized mycodermic body probably very close to brewer’s yeast. But the difficulties of the subject are only half resolved. Its complication is extreme. Lactic acid is the main product of fermentation to which it gave its name….”
- No longer was “spontaneous generation” responsible for fermentation
1855
1855 – Max von Pettenkofer (1818-1901) founder of scientific hygiene and sanitation, in 1855 “had suggested that healthy human carriers could transmit cholera, but this hypothesis was not substantiated until the end of the century.” – REF [Asymptomatic infection conceived]
1853
1853 – In 1853 the Anti-Vaccination League was formed in London – REF
1853 – Vaccination Act 1853, compulsory vaccination policy was introduced into parliament by Lord Lyttelton, as a private member. The bill passed through both Houses without opposition, and with hardly any debate except on points of detail – REF The benefits of vaccination was simply believed
- “The expediency of making vaccination universal I took, as I believed, on common notoriety, and the medical authorities I chiefly consulted were Dr. Seaton and Dr. Marson.” Lord Lyttelton in 1869, in reply to what evidence he had to bring in the bill
- In the House of Lords he said, “It is unnecessary to speak of the certainty of vaccination as a preventive of the smallpox, that being a point on which the whole medical profession had arrived at complete unanimity.”
- “The Act of Parliament of 1853 had no section devoted to the “Definition of Terms”; there was no definition of cowpox or genuine vaccine, an omission all the more remarkable that variolous matter was then being used as vaccine, on the pretext that it had “ passed through the cow. Although a medical dogma was therein established by the State, the doctrine was not formulated….”
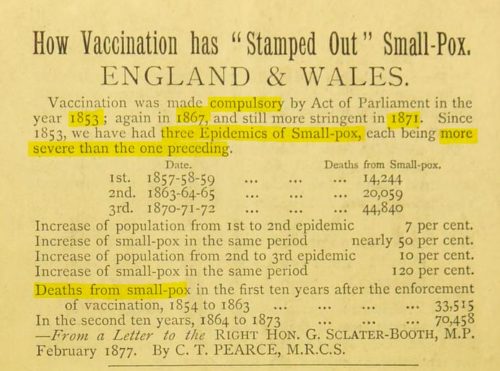
1847
1847 – “Oliver Wendell Holmes (1809-1865), in 1847, independently had discovered the clue to puerperal fever. As the latter put it, “Puerperal fever is caused by conveyance to the pregnant woman of putrid particles derived from living organisms, through the agency of the examining fingers.” Because of backlash and abuse “Holmes retracted his professorial settee to seek solace in the arms of literature…” – REF
1840
1840 – Source of polio-like disease noted as first appearing in the US in1840 as noted in The Homeopathic Recorder (1916) p 527 – READ Souce in 1984 noted as smallpox vaccine
A man told us the other day that this disease [poliomyelitis like symptoms] first appeared in 1840. It appeared after the practice of inoculating calves with small-pox virus for the production of vaccine lymph was tried. That, he said, was the source of the disease at that period.
The Homeopathic Recorder (1916) p 527
1804
1804 – In 1804, Georg Gottfried Zinke first transmitted rabies from a rabid dog to a normal one, and from dog to a rabbit and a hen, by injection of saliva. This proved that the disease was infectious. Rabies was known as hydrophobia – REF